Sea Slug
Nudibranchia
All sea slugs have both male and female sex organs
Advertisement
Sea Slug Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Mollusca
- Class
- Gastropoda
- Order
- Nudibranchia
- Family
- Opistobranches
- Genus
- Nudibranch
- Scientific Name
- Nudibranchia
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Sea Slug Conservation Status
Sea Slug Facts
- Main Prey
- Plankton, plant matter, jelly fish
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- All sea slugs have both male and female sex organs
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Biggest Threat
- Water pollution
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Colorful patterns
- Other Name(s)
- Pteropods, gastropod mollusks
- Gestation Period
- 5-50 days
- Optimum pH Level
- 7.5-8.4
- Habitat
- Shallow and deep areas of oceans
- Predators
- Fish, lobsters, crabs, humans
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Favorite Food
- Algae
- Type
- Herbivore
- Common Name
- Sea Slug
- Average Clutch Size
- 500
View all of the Sea Slug images!

Sea Slugs are tiny animals known for their bright colors and intricate patterns.
One of the most important facts to remember about sea slugs is there are over 2,000 species. They are found in both shallow and deep areas of oceans. In Asia, sea slugs are a form of cuisine.
3 Incredible Sea Slug Facts!
- Poisonous skin: Some sea slugs eat prey that contains poison. Instead of killing them, this animal stores the poison and releases it as protection against predators.
- Male and female: All sea slugs contain both male and female organs. So, when they mate with another animal they both release eggs.
- Cannibals: Sea slugs are known to eat each other. They may eat a dead sea slug or attack a live one to eat it. Not surprisingly, animals that are larger in size usually prey on smaller ones.
You can check out more incredible facts about sea slugs.
Classification and Scientific Name
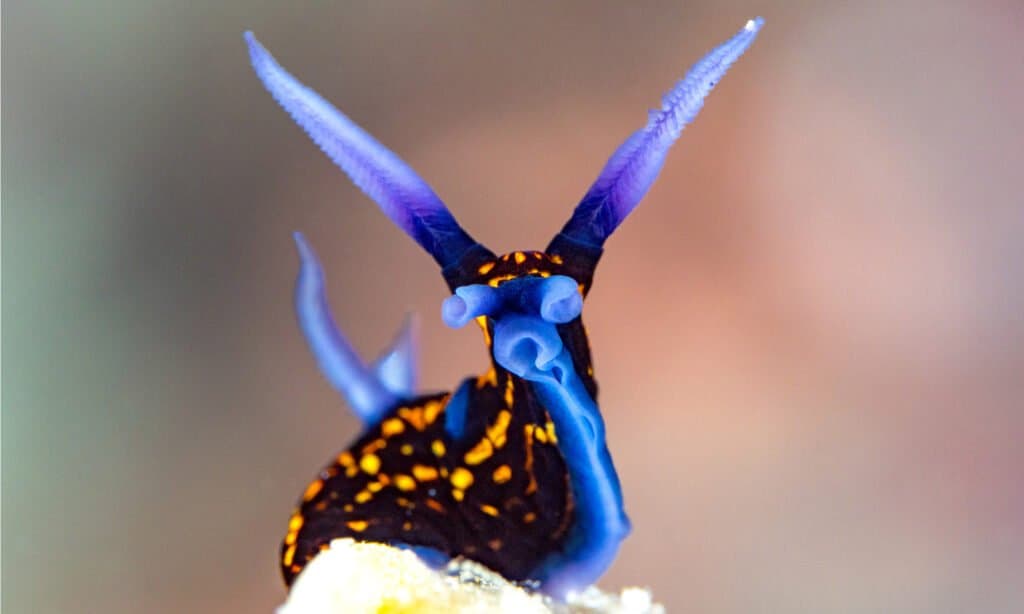

Sea slugs are a type of marine gastropod mollusk that come in a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and colors.
©Mike Workman/Shutterstock.com
The scientific name of a sea slug is Nudibranchia. The name Nudibranchia is Latin for naked gills. This refers to the animal’s lack of a shell as well as the feather-like gills and horns on its body. These animals are also called gastropod mollusks and pteropods.
There are over 2,000 species of sea slugs. In short, sea slug is a common name standing for many types of these animals. They belong to the Gastropoda class, the family of Opisthobranchs, and are in the phylum Mollusca.
Here is a list of sea slugs:
- Blue glaucus
- Sea bunny
- Leaf slug
- Black sea hare
- Hypselodoris festiva
- Spanish dancer
- Thecacera pacifica
- California sea hare
- Peltodoris atromaculata
- Clione limacina
- Melibe viridis
- Chromodoris lochi
- Elysia crispata
- Aplysia dactylomela
- Aplysia fasciata
- Notodoris minor
- Dolabella auricularia
- Aplysia punctata
- Nembrotha kubaryana
- Chromodoris willani
- Hypselodoris bullocki
- Glaucus marginatus
- Melibe leonina
- Jorunna funebris
- Chromodoris annae
- Chelidonura varians
- Spanish shawl
- Nembrotha cristata
- Chromodoris magnifica
- Pteraeolidia ianthina
- Cyerce nigricans
- Dwarf sea hare
- Aeolidia papillosa
- Vayssierea elegans
- Dirona albolineata
- Flabellina affinis
- Chromodoris quadricolor
- California aglaja
- Hypselodoris infucata
- Doriprismatica atromarginata
- Aplysia depilans
- Coryphellina exoptata
- Chromodoris elisabethina
- Aplysia juliana
- Chelidonura hirundinina
- Felimare picta
- Nembrotha chamberlaini
- Chromodoris dianae
- Hypselodoris tryoni
- Vayssierea felis
- Aplysia kurodai
Species
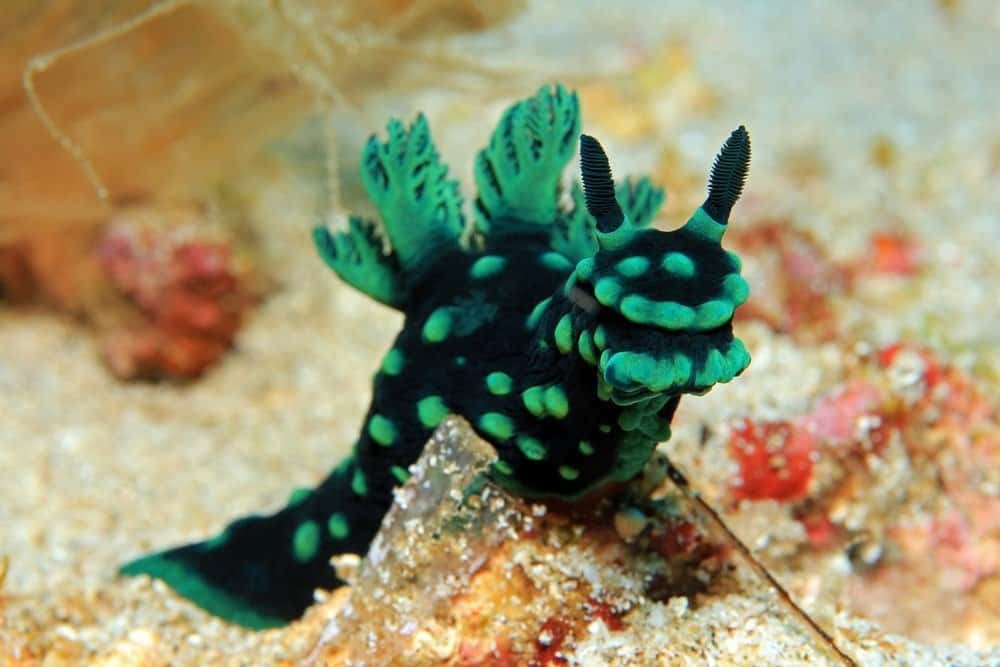

Many sea slugs have developed unique and fascinating adaptations to help them survive in their environments, such as camouflage, toxic secretions, and the ability to steal genes from other organisms.
©Daniel Lamborn/Shutterstock.com
There are species of this animal living throughout the world. There happen to be 8 species living in the Chesapeake Bay. The level of salinity in the Chesapeake Bay makes this an ideal environment for them. Some of the types living in the bay include:
- The bushy-backed nudibranch: This animal could easily be mistaken for an underwater plant. It has what appear to be prickly branches sticking out of its back. It can be brown to gray in color and is just 2 inches long.
- The ridge-backed nudibranch: The ridges all over this animal’s body earned it the name ridge-backed nudibranch. It’s white/yellow in color and lives under rocks and within gatherings of seaweed.
- The striped nudibranch: This animal measures 3-6 inches in length. It’s brown with a pattern of white stripes. Its rhinophores (scent receptors) look like two small clubs.
- The frosty-tipped nudibranch: This animal is known by the white tips on the cerata, or horns, on its back. They are yellowish in color and their skin has an opaque appearance.
Evolution and Origins
Sea slugs, which are “real plant-animal hybrids,” are animals that can synthesize food as a result of symbiosis. Green algae were consumed by the sea slugs’ ancestors. The algae entered the animal’s tissue rather than being digested, which allowed the mammal to acquire photosynthetic genes. Adult sea slugs don’t eat anymore.
There are probably repercussions from shrinking the shell, which slugs evolved from snails by doing. Yes, the majority of slugs have internal shells. a snail has a large enough external shell for the body to retract into.
Many aeolid nudibranchs consume cnidarians—animals with stinging cells like corals and jellies—and can defend themselves by using these stinging cells. From the arctic regions to the tropics, sea slugs can be found anywhere from the shallow intertidal to the deep sea.
Diversity
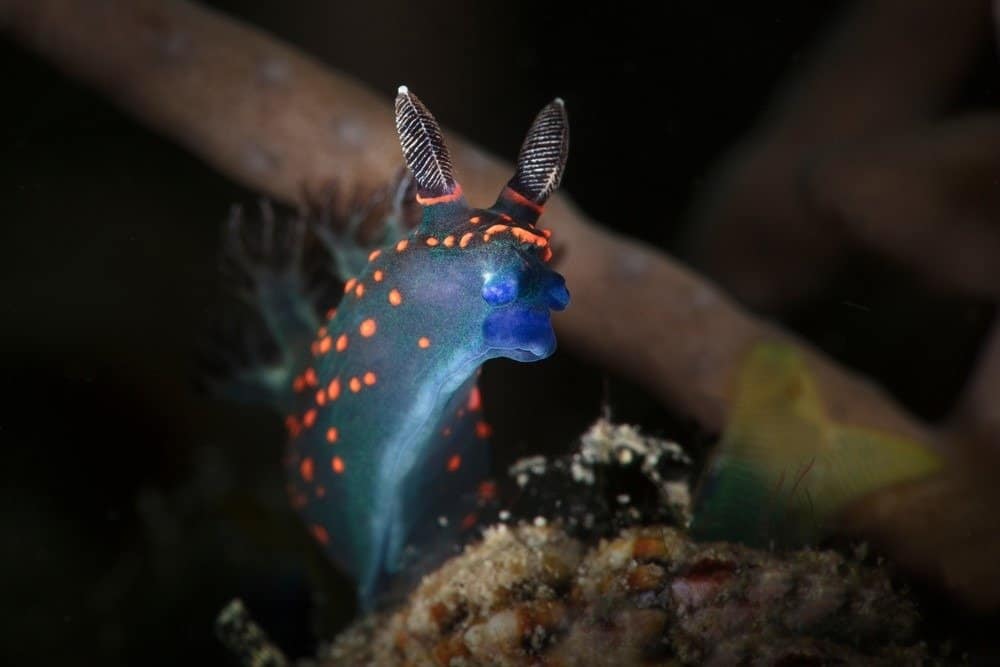

Some sea slugs are herbivores, while others are carnivores, and still others practice a form of symbiotic feeding with algae or other organisms.
©Oksana Maksymova/Shutterstock.com
Like many nudibranchs, sea slugs can store and use stinging cells or better known as nematocysts from their prey in their finger-like cerata. Although some species of sea slugs like the Pyjama slug may use their colors to express their danger level to prey.
The lettuce sea slug has ruffled lines across its body and has a process of absorbing chloroplast from the algae it eats. These cells then photosynthesize into sugars. The ruffles of the lettuce sea slug actually increase the slug’s surface area which allows the cells to absorb more light.
Headshield slugs such as the Chelidonura varians use their heads to dig into the sand where they spend most of their lives. This shield protects them from the sand entering their mantle during burrowing.
There are many different types of sea slugs which proves it vast diversity of the species.
Appearance
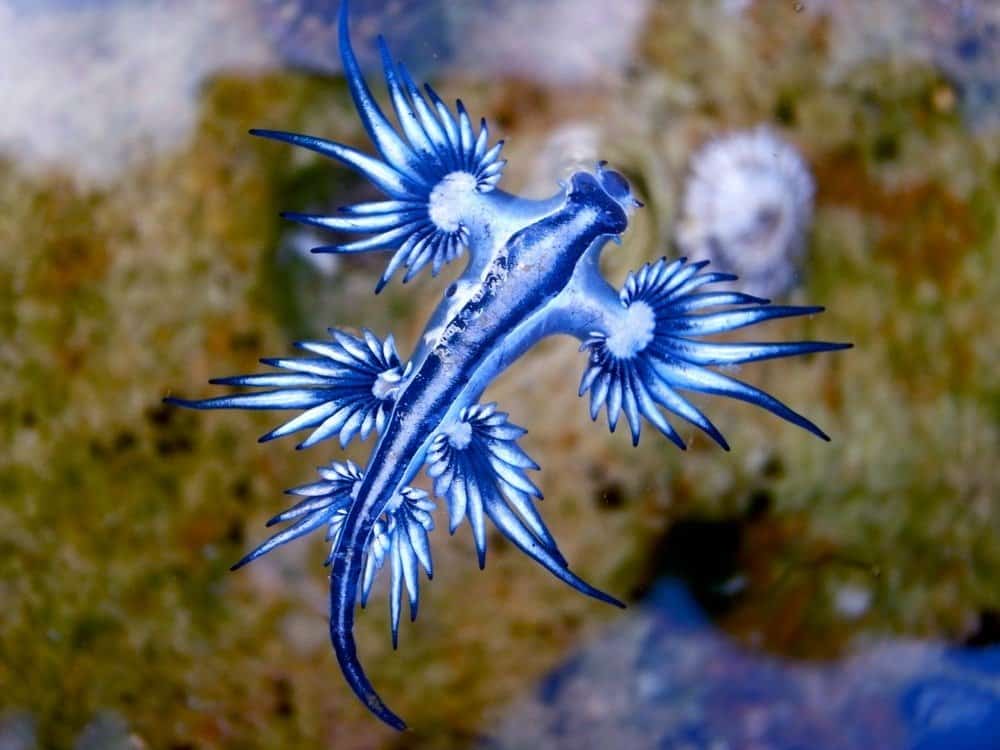

Sea slugs play an important role in their ecosystems as both predator and prey, and they are also used in biomedical research to study topics such as cancer and nerve regeneration.
©Sahara Frost/Shutterstock.com
The appearance of these animals depends on their species. Most of them have cerata on their body. Also, most have rhinophores, or scent receptors, on the top of their head. They can range from one-eighth of an inch to 12 inches in length. Furthermore, they can weigh up to 3.3 pounds.
One of the most colorful types is known as the blue dragon. It has a blue body, dark blue stripes on its head, and silver on its back. One of the most interesting facts about this animal is its cerata look like slim fingers on both sides of its body. It usually grows to be 1.2 inches in length.
The Spanish dancer is another notable animal belonging to the phylum Mollusca. Its flat body is bright orangish-red. It can grow to be 11 inches long. It folds and unfolds itself as it swims.
The black sea hare is an exception to the small size of most of these animals. It is the largest species measuring 39 inches and weighing 31 pounds!
While some sea slugs feature colors that blend into their underwater habitat, others have toxins in their skin that help to fend off predators.
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
These animals live in oceans throughout the world. They live along the eastern and western coasts of both North and South America. They live off the coast of Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australia. They live in temperate to tropical areas of saltwater. Some live in shallow areas while others live at depths of 2,300 feet beneath the surface.
The Blue Glaucus also known as the blue dragon sea slug is considered Endangered. This is due in part to water pollution. They’re also captured and sold on the exotic pet market.
Otherwise, the animal’s population is described as Stable. Their official conservation status is Least Concern.
Predators and Prey
What eats sea slugs?
Fish, crabs, and lobsters are all predators of these animals. Because of their small size, these animals are vulnerable to many other sea creatures. However, the poison they carry in their skin serves as an effective defense against many predators.
Humans are also predators of sea slugs. Some species are captured and sold on the exotic pet market. Others are captured and eaten.
Another environmental threat to these animals is water pollution. The official conservation status of sea slugs is Least Concern with a stable population.
What do sea slugs eat?
Plankton, algae, and jellyfish are all prey of these animals. Some of these animals are herbivores eating algae and other plant life off rocks. Others are carnivores eating plankton and other sea creatures.
Blue dragons are carnivores eating man-o-war jellyfish. As it eats the man-o-war jellyfish, the blue dragon absorbs poison from its prey and can turn the same poison on a predator.
Reproduction and Lifespan
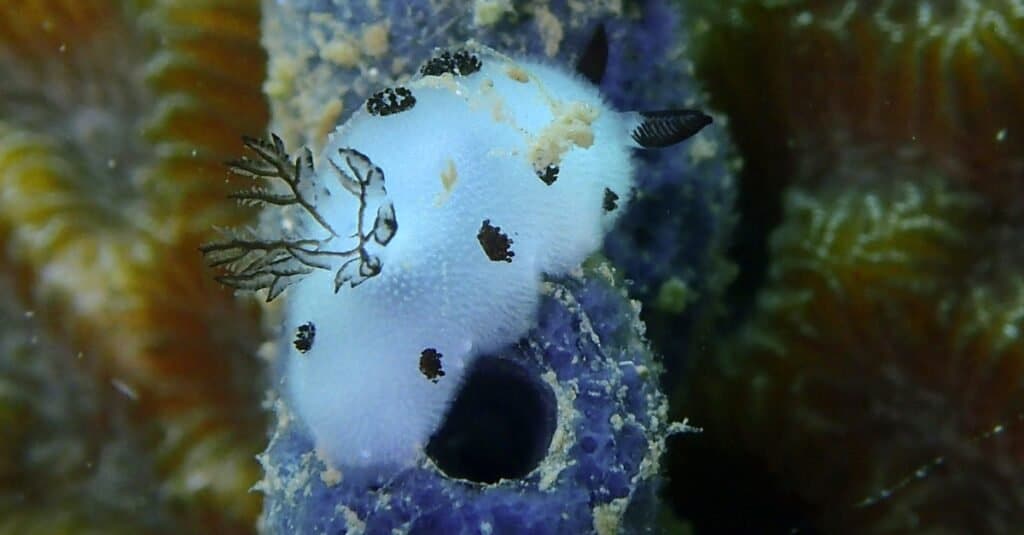

The sea bunny is a type of sea slug called Jorunna parva. Most are less than an inch (2.5 centimeters) long and can be found throughout the Indo-Pacific Ocean from South Africa to the central Pacific.
©sutapat.t/Shutterstock.com
These animals have both male and female sex organs. They lay egg masses that can sometimes contain over one million eggs. Some, like the blue dragon, lay eggs on the carcasses of their prey. Others lay their eggs on floating logs or vegetation.
The age of sexual maturity depends upon the animal’s lifespan.
The incubation period of the eggs ranges from 5 to 50 days. The animal’s lifespan is from 1 to 4 years depending on its species.
Fishing and Cooking
These animals are caught and sold in the exotic pet trade. They are slow and can easily be caught in a net.
The animal’s skin is roasted and dried. They’re eaten in China and other parts of Asia. Some have reported that they have a bitter taste due to the mucous on their skin.
When this animal is on the menu, it’s usually served with vegetables, especially mushrooms, and cabbage. They are known to be low in calories and high in protein.
View all 293 animals that start with SSea Slug FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a sea slug?
Sea slugs are small, slow-moving ocean creatures known for their bright colors and intricate patterns. They can measure an eighth of an inch long to 12 inches. Oftentimes, they have horns on their body and scent receptors called rhinophores on their head.
Where are sea slugs found?
These creatures are found in oceans throughout the world. They live in temperate to tropical waters. Sea slugs can live in shallow water or thousands of feet down in the ocean.
What do sea slugs eat?
Some sea slugs are herbivores eating algae and other plant life. Others are carnivores eating plankton, jellyfish, and other animals.Sea slugs will eat whatever prey is most abundant in their environment.
Where do sea slugs live?
They live under rocks, in crevices, and near coral reefs.
What does a sea slug look like?
A sea slug can be one color or several. Some have stripes while others have spots. Some sea slugs have horns all over their body while others are flat. It all depends on the species.
Are sea slugs dangerous?
They can be. The skin of a sea slug contains a poison that can be passed along to a human through a sting.
What Kingdom do Sea Slugs belong to?
Sea Slugs belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do Sea Slugs belong to?
Sea Slugs belong to the phylum Mollusca.
What class do Sea Slugs belong to?
Sea Slugs belong to the class Gastropoda.
What family do Sea Slugs belong to?
Sea Slugs belong to the family Opistobranches.
What order do Sea Slugs belong to?
Sea Slugs belong to the order Nudibranchia.
What genus do Sea Slugs belong to?
Sea Slugs belong to the genus Nudibranch.
What type of covering do Sea Slugs have?
Sea Slugs are covered in Smooth skin.
What are some predators of Sea Slugs?
Predators of Sea Slugs include fish, lobsters, crabs, and humans.
What is the average clutch size of a Sea Slug?
Sea Slugs typically lay 500 eggs.
What is the scientific name for the Sea Slug?
The scientific name for the Sea Slug is Nudibranchia.
What is a distinguishing feature of the Sea Slug?
Sea Slugs have colorful patterns.
What is the lifespan of a Sea Slug?
Sea Slugs can live for 1 to 4 years.
What is the biggest threat to the Sea Slug?
The biggest threat to the Sea Slug is water pollution.
What is the optimal pH for a Sea Slug?
The optimal pH for a Sea Slug is between 7.5 and 8.4.
What is another name for the Sea Slug?
The Sea Slug is also called the pteropod or gastropod mollusk.
How many Sea Slugs are left in the world?
The population size of the Sea Slug is unknown.
How fast is a Sea Slug?
A Sea Slug can travel at speeds of up to 0.2 miles per hour.
How do Sea Slugs have babies?
Sea Slugs lay eggs.
What are the key differences between sea slugs and nudibranchs?
The key differences between sea slugs and nudibranchs are size, behavior, where they are found, diet, reproduction, defense mechanism, and predators.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nudibranch
- Reef Biosearch, Available here: https://www.greatbarrierreefs.com.au/blue-seaslug/index.html
- New Heaven Reef Conservation, Available here: https://newheavenreefconservation.org/learning-resources/explore-topics/nudibranchs-and-other-sea-slugs