Drum Fish
Sciaenidae
The drum fish makes a croaking sound with its swimming bladder!
Advertisement
Drum Fish Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Perciformes
- Family
- Sciaenidae
- Scientific Name
- Sciaenidae
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Drum Fish Conservation Status
Drum Fish Facts
- Prey
- Mollusks, insects, and fish
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- The drum fish makes a croaking sound with its swimming bladder!
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat changes
- Most Distinctive Feature
- The croaking noise
- Other Name(s)
- Drum or croaker
- Gestation Period
- A few days
- Predators
- Birds, fish, and humans
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Type
- Fish
- Common Name
- Drum fish
- Number Of Species
- 275
View all of the Drum Fish images!
The drum fish lives up to its rather literal name by emitting a very loud, repetitive, throbbing noise that aids in communication with other animals.

This fish is mostly endemic to saltwater seas and oceans, but a few species reside exclusively in freshwater rivers and lakes as well. They are a very popular type of fish for both recreational and commercial purposes.
3 Incredible Facts!
- Drum fish are also called drums or croakers because of the sound they make with their swimming bladders.
- The drum fish is a regular sight at many aquariums around the world.
- Some species have whiskered barbels, like catfish, for sensing the surrounding environment.
Scientific Name
The drum fish is a member of the Family Sciaenidae, which derives from “sciaena,” the Latin name for the sea fish. (Sciaena is also the name of a specific genus within Sciaenidae.)
The entire family belongs to the order of ray-finned fish called Perciformes, which features the familiar perch, sunfish, groupers, and snappers. It is the largest order of vertebrates in the world. However, there is some debate about the classification with some biologists placing the drum fish in the Order Acanthuriformes.
Species
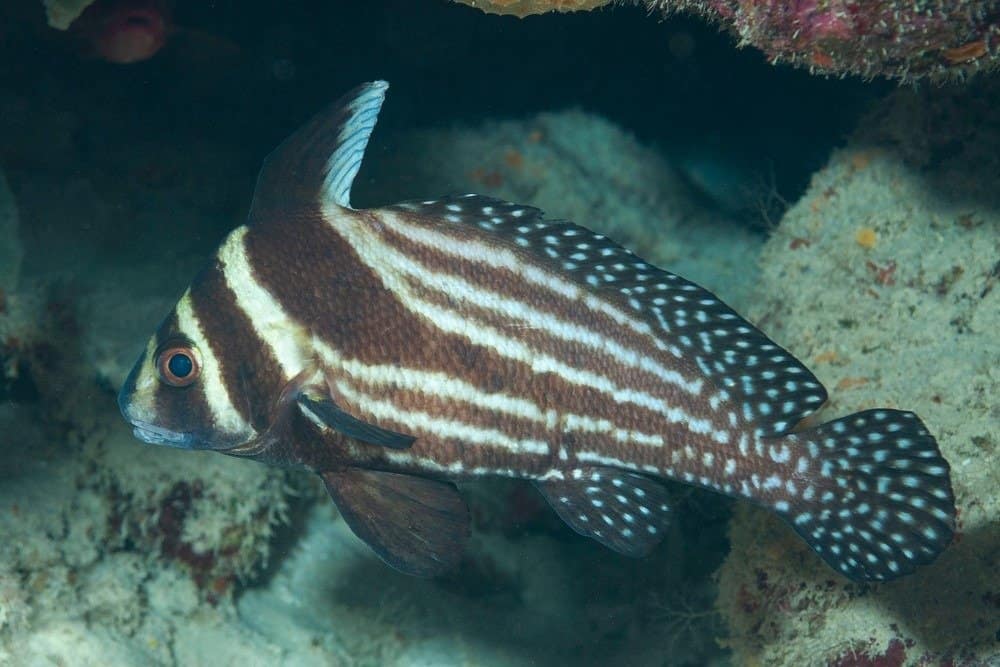

The Spotted drum fish is one over 275 species of drum fish from the Family
Sciaenidae.
©Jesus Cobaleda/Shutterstock.com
The family of drum fish includes approximately 275 (and perhaps as many as 300) species, depending on who’s counting. Here is just a small sample of them:
- Red Drum: Also known as the channel bass, this species is endemic to the Atlantic Ocean between Massachusetts and the Gulf of Mexico. Although red and white in color, it also has a black mark on the tail.
- California corbina: Also known as the California kingcroaker or kingfish, this species actually lacks the swim bladder with which it can make a croaking sound.
- Common Weakfish: Known by the Native American name of Squeteague, this endangered species inhabits the Atlantic Ocean along the East Coast of the United States. Other species of weakfish include the smooth weakfish, smalltooth weakfish, and smallscale weakfish, all of which are listed as least concern.
- Totuava: The totuava or the totoaba is the largest species of drum fish in the world. This rare species lives in the Gulf of California near Mexico.
- Freshwater Drum: This is the only drum fish species in North America (stretching from the Hudson Bay to Guatemala) that lives in freshwater rivers or lakes for its entire lifespan.
Appearance
The drum fish is a rather standard-looking, ray-finned fish with a long and rounded body, a groove or notch between the ray and spine, and two dorsal fins running along the back. Most drum fish have a small mouth, jaw, and teeth, but a few select species are specialized with a larger mouth, a jutting jaw, and sharp canine teeth. Silver is the dominant color, but many other species come in all manner of red, brown, black, and white.
By far the most important and distinguishing characteristic of this family is the presence of a large muscle attached to the swimming bladder. When it moves this muscle, the fish can greatly amplify sound, creating the loud croaking or cracking noise for which it’s named. This sound serves the purpose of attracting mates in the breeding season, which means that in some species this ability appears only in the males.
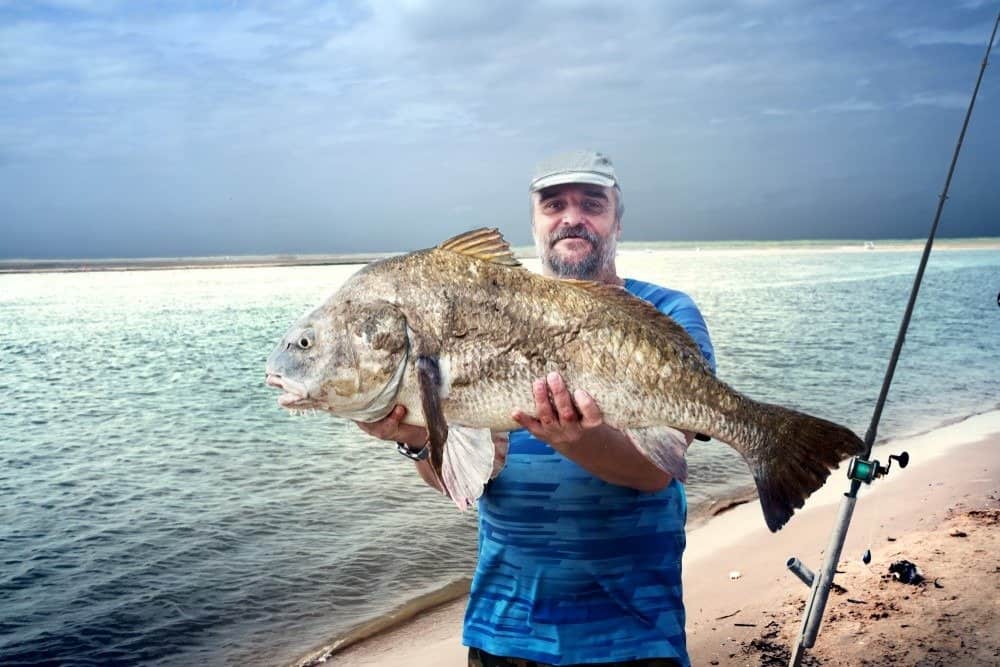

A fisherman is holding a huge black drum fish (Pogonias cromis), one of the largest drum species that can weigh 30-90 pounds.
©IrinaK/Shutterstock.com
In other species, the drum sound also serves a secondary purpose as a warning or location call throughout the entire year. Each species can be identified by the unique sound of its “vocalization.” Although this is considered to be the defining feature of the drum fish, some species such as the aforementioned California corbina lack the ability entirely.
The drum fish comes in a variety of different sizes but usually measures no more than a few feet in length and up to 60 pounds. The largest species is the truly gigantic 225-pound totuava of the Gulf of California. Saltwater fish tend to be larger than the freshwater fish.
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
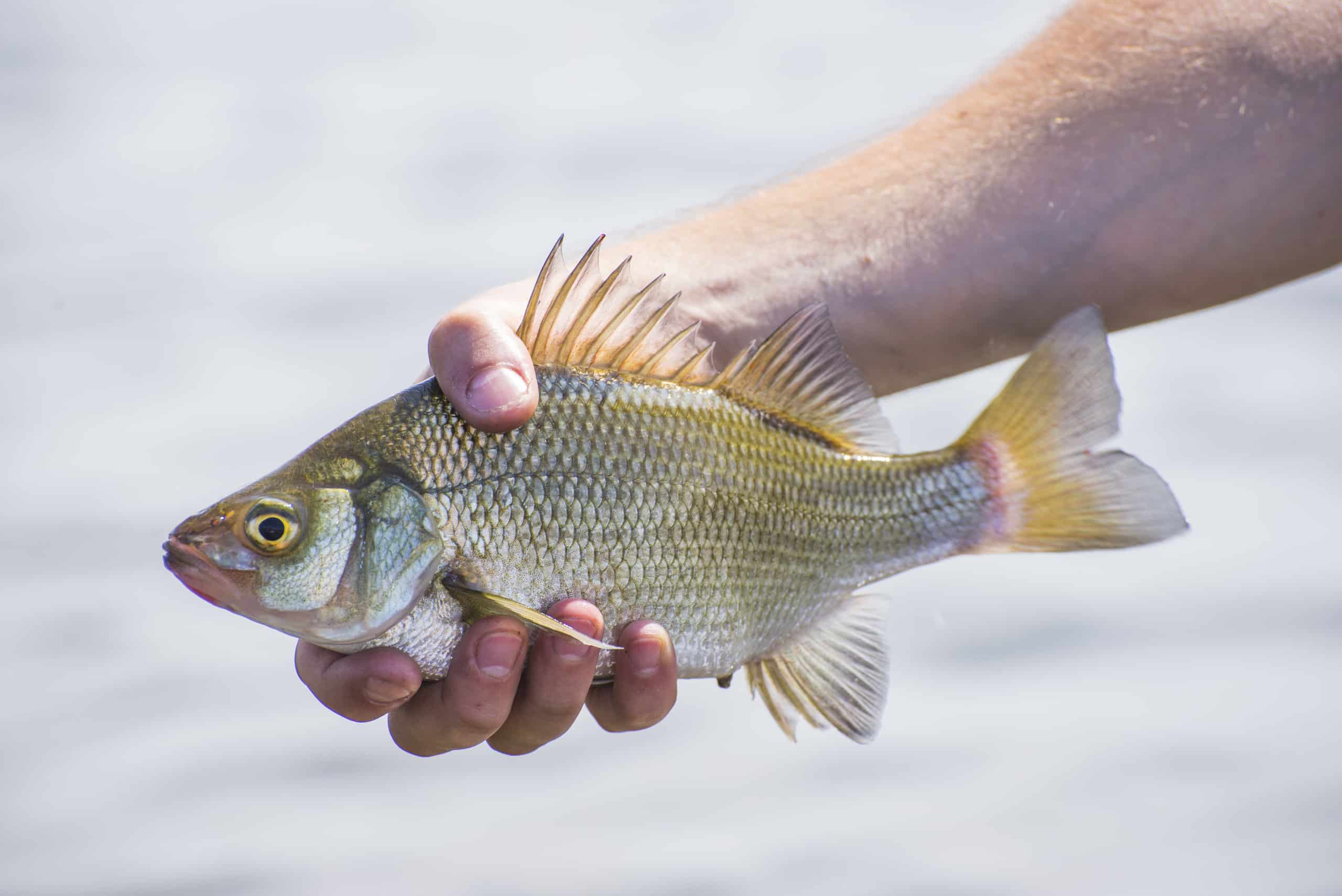

The Freshwater drum is one of the few drum species that can be found in freshwater lakes and rivers.
©Roxana Gonzalez/Shutterstock.com
The drum fish is endemic to both tropical and temperate saltwater regions around the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. The most preferential locations are the bays and estuaries near the coast. A few species inhabit freshwater lakes and rivers either partially or exclusively throughout the year. Population numbers vary by species. One of the most common species, the red drum, appears to be in stable and good health despite their popularity in commercial fishing. Most species are of least concern to conservationists, but not every species is so lucky. The aforementioned totuava is critically endangered.
Predators and Prey
Predators of the drum fish include large fish, sea birds, and humans. The drum fish is sometimes threatened with overfishing, poaching, and habitat loss from dams and the diversion of water.
The drum fish is a bottom-dwelling fish that feeds on crustaceans, mussels, insects, and other fish along the sea, river, or lake floor. The large canine teeth of some species can help them crunch through the tough exterior of crabs and other shelled prey.
Reproduction and Lifespan
Many aspects of drum fish reproduction, including spawning season and gestation period, vary by species. The most common breeding season takes place during the summer or fall months in shallow waters. The male uses its unique vocalization to attract a suitable mate. After copulating, the female can lay thousands or sometimes even millions of eggs at one time. The male then fertilizes the eggs with his sperm.
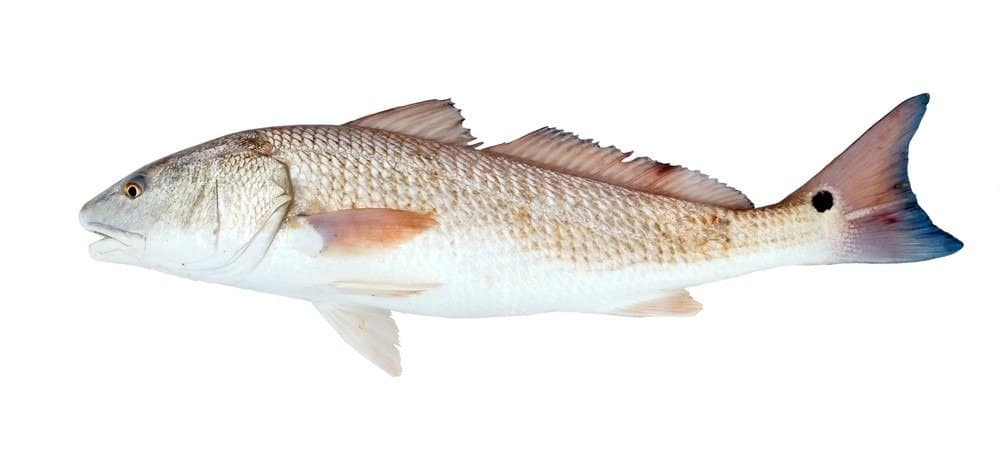

The Red drum or Redfish (Sciaenops ocellatus) spawning season takes place from August to October and generally lasts for 8 to 9 weeks.
©IrinaK/Shutterstock.com
The young larvae emerge from the eggs within a matter of days, measuring no more than few millimeters in size, and they develop into mature individuals within a few years of life. The life expectancy varies by species. The average life of the freshwater drum is six to 13 years, but some saltwater species can survive up to 50 years in the wild. More extreme ages have been documented as well.
Fishing and Cooking
The drum fish is a common catch for both commercial and recreational purposes. Recreational fishers can find these fish around the surf or pier. Commercial fishers catch large numbers in more open waters with a net. According to United Nations statistics, the drum was, at one point, the 25th most caught fish in the world.
The meat of the drum fish is sometimes described as a mild and delicate with a slightly sweet taste. The saltwater species are caught and eaten far more often than the freshwater types. In fact, fish connoisseurs often complain that the freshwater drum fish has an inferior taste. The flesh can be baked, boiled, or sautéed, and the subtle taste goes along well with a number of different seasonings, herbs, and vegetables.
View all 110 animals that start with DDrum Fish FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a drum fish?
The drum fish is a type of ray-finned fish that makes a croaking or cracking sound to communicate with others. Unless you know what you’re looking for, it may be difficult to identify this fish from its appearance alone. It doesn’t have too many distinguishing outward characteristics.
Is a drum fish a carp?
The drum fish is not the same type of fish as a carp. The carp is a freshwater fish of the family Cyprinidae. It belongs to an entirely different order (though the same class of ray-finned fish). The confusion may arise from the fact that some freshwater drums are mistaken for the carp.
Why are they called drum fish?
The name comes from the sound they make with their specialized muscles for the purpose of communication. This croaking sound is produced by the vibration of the muscle against the swimming bladder, kind of like the beating of a drum; hence, the name.
Are drum fish bottom-feeders?
Yes, drum fish spend most of the time in the benthic zone. This is the lowest level of any body of water, including seas, oceans, rivers, and lakes. They consume small animals that live along the floor. Some species have big mouths, powerful jaws, and sharp teeth for consuming hard-shelled creatures.
Can you eat drum fish?
Yes, the drum fish is a very edible creature, but the saltwater drum is generally preferred over the freshwater drum. The freshwater drum is considered to be a “rough fish” by many fishers, meaning it is not quite as desirable to catch or eat.
Are Drum Fish herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Drum Fish are Carnivores, meaning they eat other animals.
What Kingdom do Drum Fish belong to?
Drum Fish belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do Drum Fish belong to?
Drum Fish belong to the phylum Chordata.
What class do Drum Fish belong to?
Drum Fish belong to the class Actinopterygii.
What family do Drum Fish belong to?
Drum Fish belong to the family Sciaenidae.
What order do Drum Fish belong to?
Drum Fish belong to the order Perciformes.
What type of covering do Drum Fish have?
Drum Fish are covered in Scales.
What are some predators of Drum Fish?
Predators of Drum Fish include birds, fish, and humans.
In what type of habitat do Drum Fish live?
Drum Fish live in rivers, lakes, estuaries, and bays.
What is the scientific name for the Drum Fish?
The scientific name for the Drum Fish is Sciaenidae.
What is the lifespan of a Drum Fish?
Drum Fish can live for up to 50 years.
How many species of Drum Fish are there?
There are 275 species of Drum Fish.
What is a distinguishing feature of the Drum Fish?
Drum Fish make a croaking noise.
What is the biggest threat to the Drum Fish?
The biggest threat to Drum Fish is habitat changes.
What is another name for the Drum Fish?
The Drum Fish is also called the drum or croaker.
How many Drum Fish are left in the world?
The population size of the Drum Fish is unknown.
What is an interesting fact about Drum Fish?
The Drum Fish makes a croaking sound with its swimming bladder!
How do Drum Fish have babies?
Drum Fish lay eggs.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/drum-fish
- Seafish, Available here: https://www.seafishpool.com/sciaenidae-drums-croakers/