Tree Frog
Found in warmer jungles and forests!
Advertisement
Tree Frog Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Tree Frog Conservation Status
Tree Frog Facts
- Lifestyle
- Solitary
- Favorite Food
- Insects
- Type
- Amphibian
- Average Clutch Size
- 50
- Slogan
- Found in warmer jungles and forests!
View all of the Tree Frog images!
Tree frogs are some of the world’s most whimsical amphibians, thanks to their cute eyes and unique legs and toes that allow them to climb trees easily.

Unlike their somewhat dumpy terrestrial counterparts, tree frogs generally have bright colors that make them a favorite zoo exhibit. Their distinctive calls often make them heard and not seen in their native habitat as they are primarily active at night. Although these frogs live mostly in tropical climates, some species live in more temperate areas and hibernate during the winter.
5 Incredible Facts!
- In Europe, these frogs were historically seen as barometers because they would respond to approaching rain by barking.
- Most of these frog species can change skin color, sometimes because of their mood, among a range of green, gray, brown, and yellow hues.
- White’s tree frogs have a strong sense of hearing and can sense vibrations through the ground.
- Red-eyed tree frogs are considered to be the ambassadors of these frog species because of their strikingly vivid eyes.
- These frogs have an additional eyelid that veils their eyes. They also blink when swallowing to force down their prey.
You can check out more incredible facts about tree frogs.
Scientific Name and History
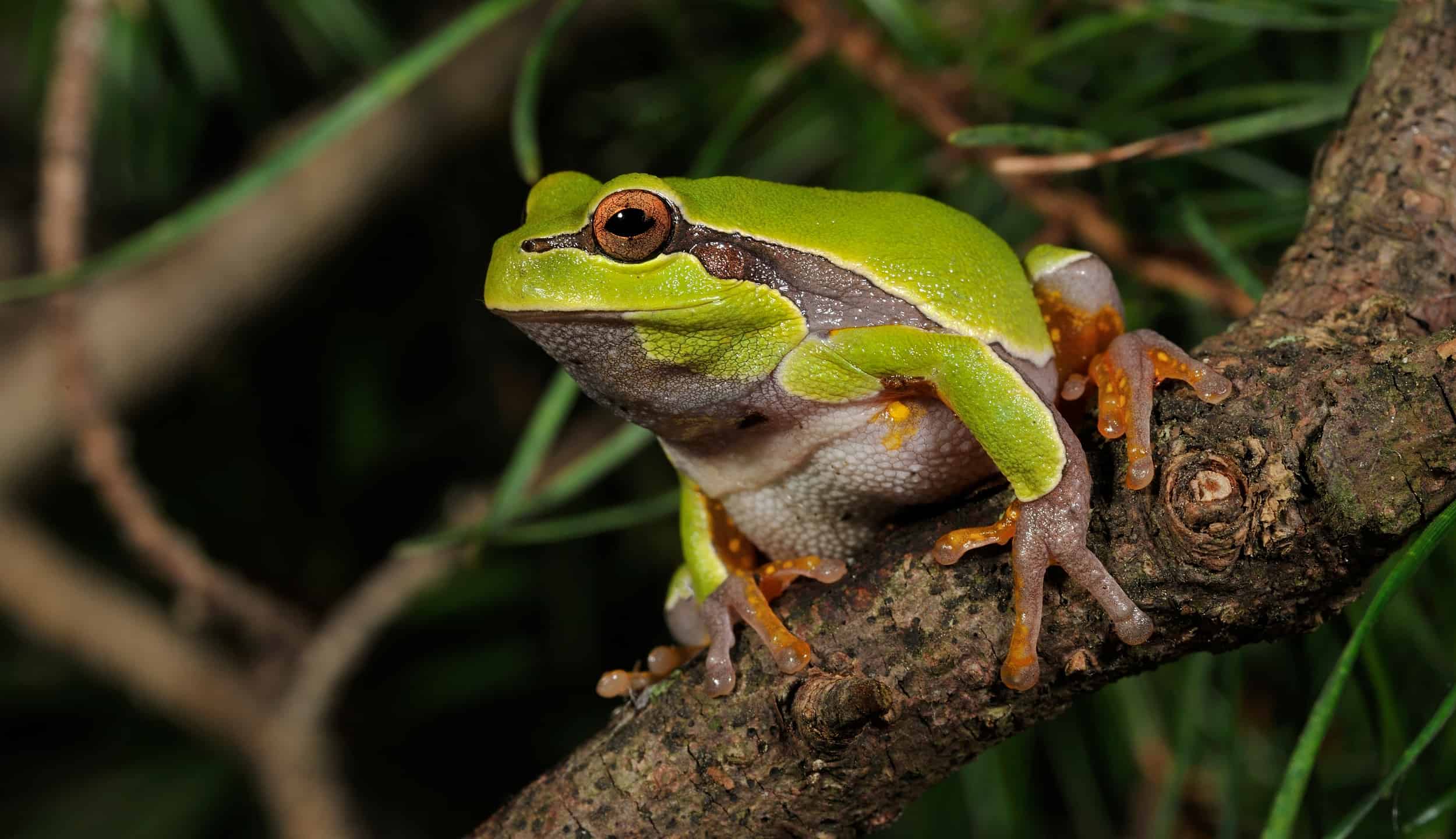

The Pine Barren Treefrog (
Hyla andersonii) is a member of the family
Hylidaeand thus is one of the “true” tree frogs.
©Breck P. Kent/Shutterstock.com
Tree frogs comprise several families of the order Anura. Those in the family Hylidae with the scientific name Hyla are sometimes called true tree frogs and are the most numerous — about 700 species in 40 or so genera. Nonhylid tree frogs have scientific names that incorporate the families Centrolenidae, Hyperoliidae, Rhacophoridae, and Microhylidae.
Frogs have lived on Earth for about 100 million years. There is fossil evidence that the red-eyed tree frog has remained much the same for more than 10 million years. The reason there are so many different species from several different biological families is a process called convergent evolution; that is, similar living conditions have caused them to evolve to look very similar.
To the ancient Egyptians and Mesopotamians, frogs symbolized fertility, while to the ancient Greeks and Romans, frogs represented not only fertility, but also harmony and licentiousness. Frogs have been popular characters in folklore and fairy tales, including the frog that turned into a prince when kissed by the fair maiden.
Types of Tree Frogs
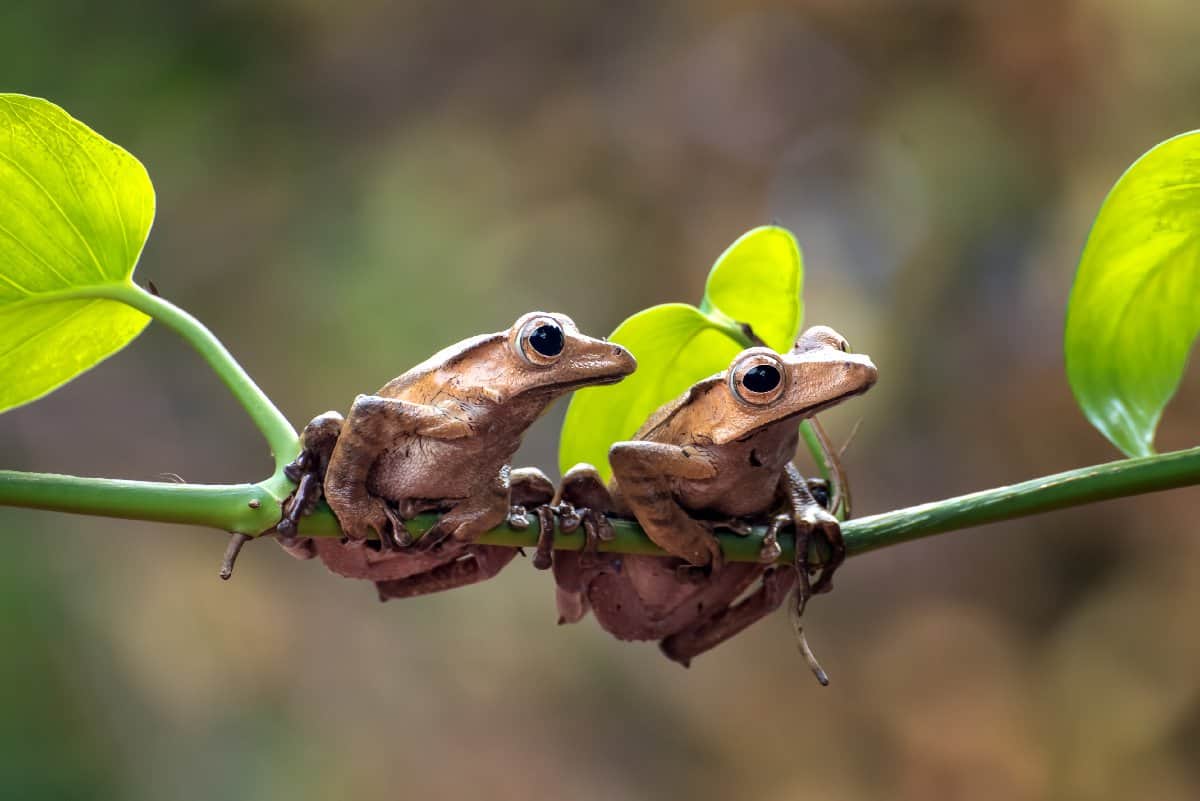

The Borneo Eared Frog (
Polypedates otilophus,family
Rhacophoridae
) is
endemic
to
Borneo
but lives also in
Brunei
,
Indonesia
, and
Malaysia
©iStock.com/DikkyOesin
Although there are far too many types of tree frogs to name here, a few notables include:
- White-lipped tree frog – largest, lives in Australia and Oceana
- Cuban tree frog – largest in Western Hemisphere, lives in Caribbean and southeastern U.S.
- Red-eyed tree frog – flashing, bulging eyes; has remained relatively unchanged for 10 million years, lives in southern Mexico, Central America and northern South America.
- American green tree frog – bright green, uses a variety of barking calls for communication
- White’s tree frog (aka dumpy tree frog or Australian tree frog) – encase their bodies in caerviein to preserve moisture, live in Australia and New Guinea.
- Gray tree frog – lives in North America
- Little grass frog – smallest of all tree frogs, lives in cypress swamps of Virginia, Florida and Alabama.
- Boophis (aka bright-eyed or skeleton) tree frog – the only genus in the subfamily Boophinae; lives on Madagascar and Mayotte Island.
- Other names you might come across are the European green frog, the spring peeper, the pine barren tree frog, the Borneo eared tree frog, Cope’s gray tree frog, and the Pacific tree frog, which is the frog that makes the famous “ribbit” sound attributed to all frogs on TV and in the movies.
More detail about these frogs appears below.
Appearance
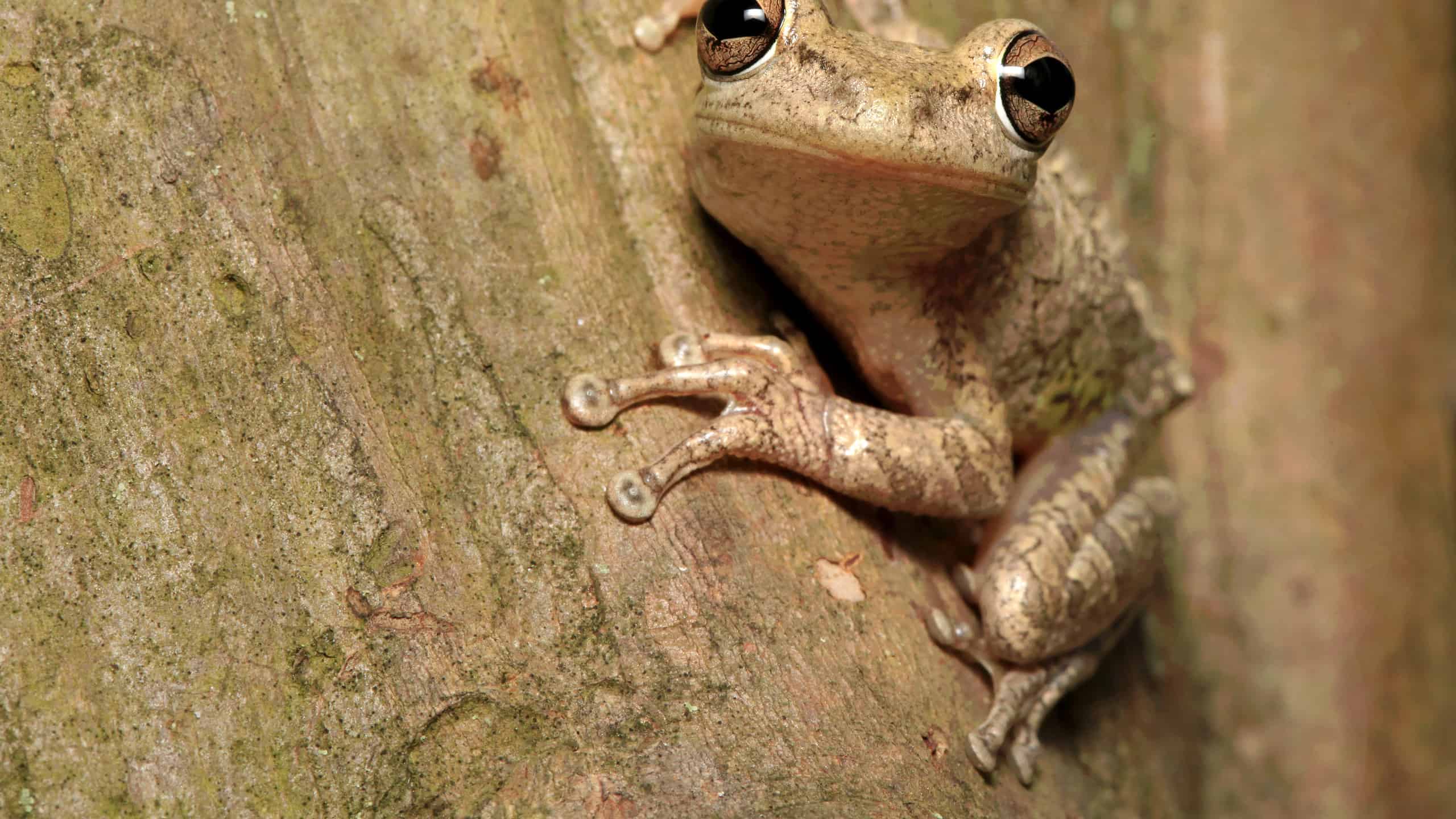

This Cuban tree frog is showing off his distinctive feet with their odd toe bones and toe pads.
©Steve Bower/Shutterstock.com
The most distinguishing feature of the tree frogs is their feet, as the last bone in their toes is claw-shaped. Toe pads with tiny suction cups and extraskeletal structures on their toes also help them climb trees. They come in a variety of colors, most commonly green, gray, or brown.
Because of the primarily arboreal habitat that finds them living on leaves and small branches, most of these frogs are small in size and typically more slender than terrestrial frogs. The smallest species are less than an inch in length.
The largest of these frogs are the white-lipped tree frog found in Australia and Oceana, ranging from four inches to 5.5 inches long. The largest species in the Western Hemisphere is the Cuban tree frog, found in the Caribbean and the southeastern United States with a length of 1.5 to five inches. It is brown and somewhat bland and dumpy in appearance.
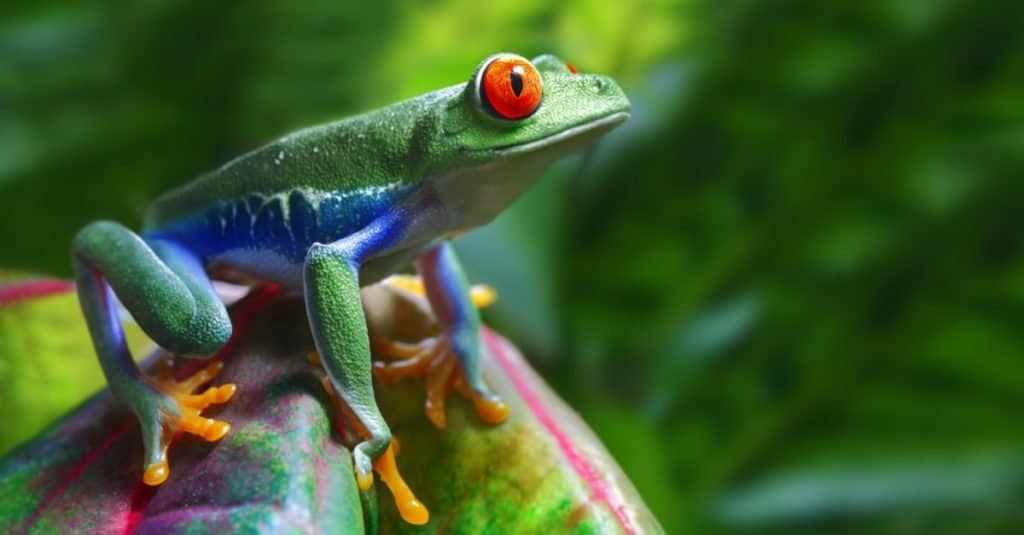

The red-eyed tree frog can flash its bulging eyes to reveal their bright body colors and startle prospective predators.
©Brandon Alms/Shutterstock.com
As one of the most striking members of the Hylidae family, red-eyed tree frogs may have developed their bright eyes, in part, so that predators may question their meal choice and go for a less intimidating prey. Another adaptation, called startle coloration, allows red-eyed tree frogs to flash their bulging eyes and reveal webbed orange feet and their bright blue-and-yellow flanks, often causing birds and snakes to stop in surprise, which gives time for the frog to flee. Their bright green color may also overstimulate predators’ eyes by creating a confusing ghost image.
American green tree frogs are a bright green, which helps them camouflage in surrounding foliage in the wild. They have a light white or cream-colored stripe from the side of the head down to their flanks.
White’s tree frogs encase their bodies in a milky white coating called caerviein that helps them survive in dry areas by conserving body moisture. Scientists have used extracts from their skin for medicines that fight staphylococcus bacteria, lower blood pressure, and treat cold sores caused by the herpes virus.
Behavior
Most species are nocturnal and solitary but will gather in large groups during mating season. Many spend their days sleeping on leaves and branches. In hot summer months, White’s tree frogs often go looking for water in people’s homes. When threatened, they emit an ear-piercing scream. Green tree frogs use a variety of barking calls for communication. Adults will frequently camouflage themselves in vegetation by tucking in their legs and closing their eyes.
Habitat
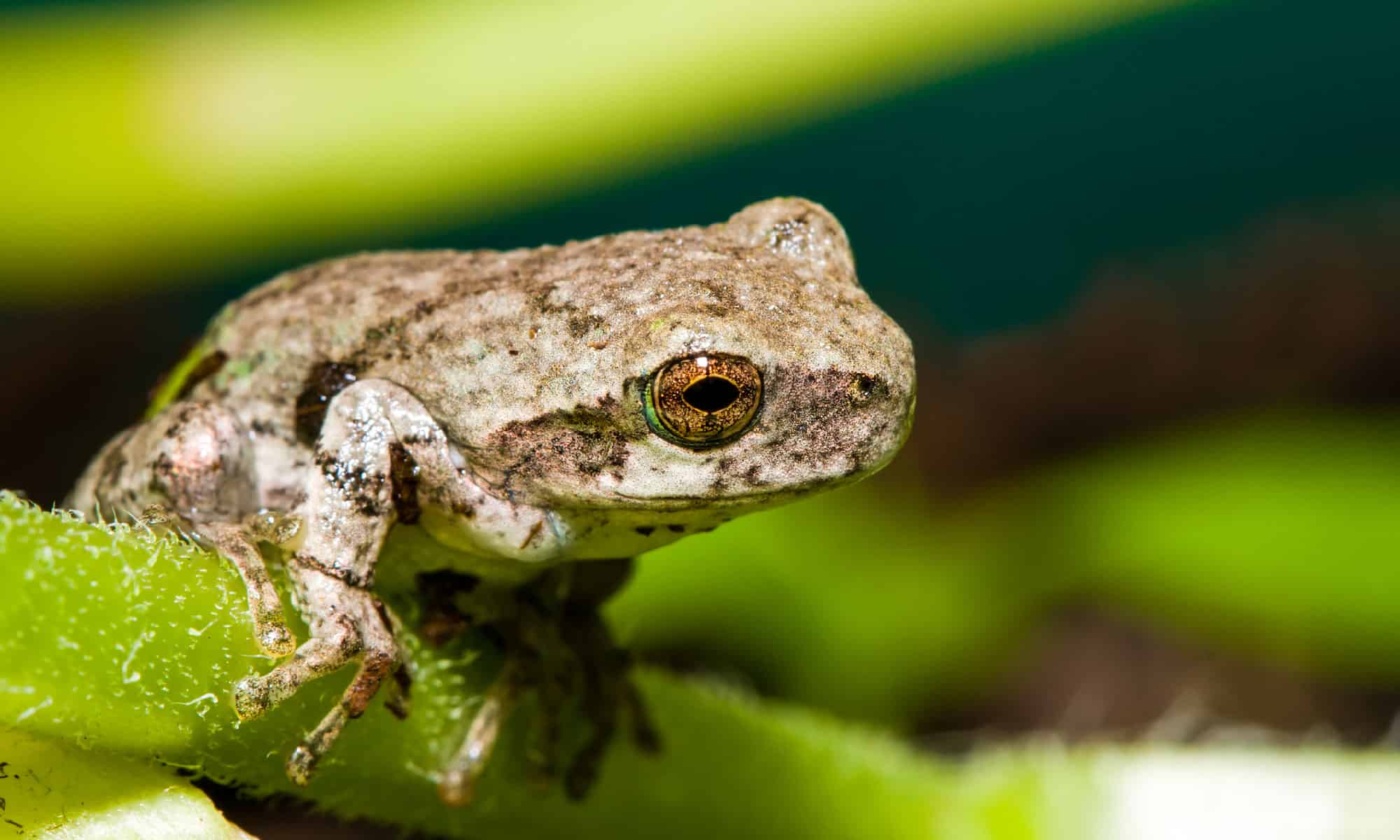

This Cope’s gray tree frog, which is almost identical to the gray tree frog, also lives in North America.
©iStock.com/Coffee999
Tree frogs live on every continent except Antarctica, with the highest concentration in Central and South America, where you will find about 600 species. About 30 species live in the warmer regions of the southeastern United States. Most, but not all, species are arboreal, which is why they have long legs and toe pads to help them climb and jump. Non-arboreal species live in lakes and ponds or among moist ground cover.
Red-eyed frogs live in tropical lowlands from southern Mexico, through Central America and into northern South America. They are nocturnal, hiding in the rain forest canopy.
An adaptable species called White’s tree frogs live in Australia and New Guinea. They prefer moist forests and typically do not live near bodies of water, collecting rainwater that collects on leaves and in cup-shaped plants and crevices. This species’ adaptability allows them to live in suburban and agricultural areas with people and is commonly found in bathrooms, water tanks, and reservoirs.
Diet
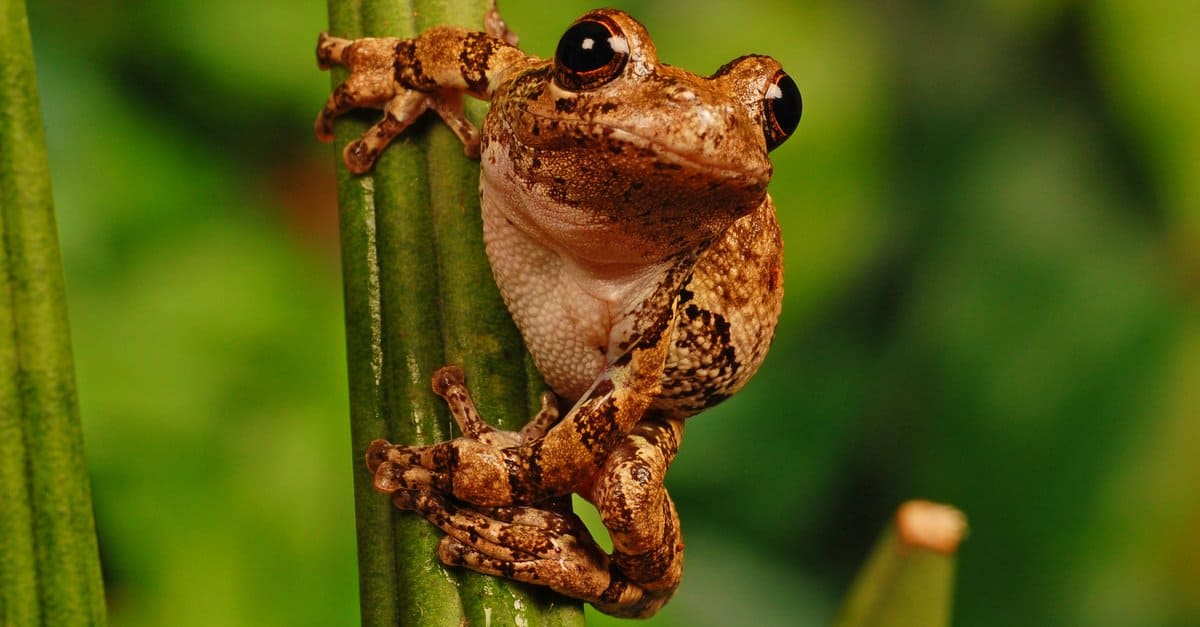

Tree bark is the most common element the gray tree frog imitates.
©Deatonphotos/Shutterstock.com
Like other amphibians, these frogs are carnivores, eating insects like crickets and flies, worms, spiders, moths, and other invertebrates. The large Cuban frog will eat anything that will fit in its mouth, including lizards, snakes, small mammals, and even other frogs. These frogs ambush their unsuspecting prey with their long, sticky tongues. For a complete list of foods tree frogs eat, check out our “What Do Tree Frogs Eat?” page.
Predators and Threats
Predators include a variety of mammals, reptiles, birds, and even some large fish, mainly due to the frog’s small size. The official conservation status of these frogs is stated as least concern, because of their wide distribution and assumed large population. Nevertheless, these frogs experience threats to their overall population, including habitat destruction by humans, pollution, climate change, and disease. Habitat destruction is a concern in Europe, although conservation efforts in several European countries have successfully rebuilt some tree frog habitats.
Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
The males of almost every species attract mates via barking calls, with each tree frog type having its unique call.
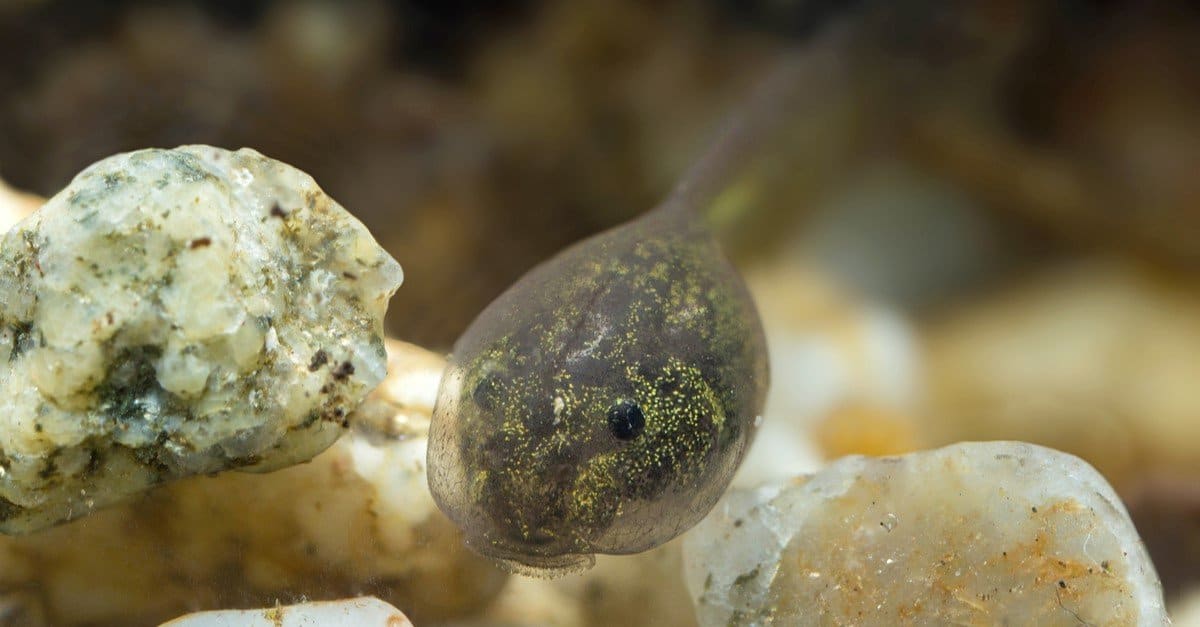

The green tree frog hatches as a tadpole that is dropped into the water to develop into an adult.
©Macrolife/Shutterstock.com
Some hatch as miniature adults, but more commonly, these frogs hatch as tadpoles that develop into adults. Females lay eggs on leaves above water, allowing hatched tadpoles to drop into the water to develop. The metamorphosis from tadpole to adult can take a few weeks to a few months.
White’s tree frogs begin to reproduce in their second year and often feast for several days before mating. Males develop a black pad on their thumbs to help grip females during mating. Clutch size varies according to species and can contain 150 to 1,000 eggs, with hatching beginning about 28 to 36 hours after laying.
Lifespan varies among species, with some living less than three years. Gray tree frogs in North America live about five years, while the Australian tree frog can live as long as 15 years in captivity. White’s tree frogs generally live about 16 years and have lived as long as 21 years in captivity.
Population
Scientists have no real estimation of the worldwide population of these frogs as they are widespread and are not endangered. However, their populations are thought to be declining as humans continue to encroach on their habitats.
In the Zoo
The Smithsonian National Zoo in Washington DC keeps red-eyed tree frogs along with White’s tree frog. Both species receive a diet of crickets, cockroaches, and worms. The best time to see these frogs in the zoo is in the early morning and late afternoon. They are primarily nocturnal creatures, so most of the time, visitors will see them sleeping on top of green leaves in their exhibit. You’ll have to look carefully, though, as these frogs tend to blend in with their environment.
View all 133 animals that start with TTree Frog FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Tree Frogs herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Tree Frogs are Carnivores, meaning they eat other animals.
What Kingdom do Tree Frogs belong to?
Tree Frogs belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Tree Frogs belong to?
Tree Frogs belong to the class Amphibia.
What phylum to Tree Frogs belong to?
Tree Frogs belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Tree Frogs belong to?
Tree Frogs belong to the family Hylidae.
What order do Tree Frogs belong to?
Tree Frogs belong to the order Anura.
What type of covering do Tree Frogs have?
Tree Frogs are covered in permeable skin.
In what type of habitat do Tree Frogs live?
Tree Frogs live in forests, woodlands, and marshes.
What is the main prey for Tree Frogs?
Tree Frogs prey on insects, worms, small frogs.
What are some predators of Tree Frogs?
Predators of Tree Frogs include birds, mammals, and reptiles.
How many eggs do Tree Frogs lay?
Tree Frogs typically lay 50 eggs.
What is an interesting fact about Tree Frogs?
Tree Frogs are found in warmer jungles and forests!
What is the lifespan of a Tree Frog?
Tree Frogs can live for 2 to 4 years.
How fast is a Tree Frog?
A Tree Frog can travel at speeds of up to 10 miles per hour.
Where do tree frogs live?
Every continent, except Antarctica, provides a home to tree frogs. They usually live in tropical or semi-tropical climates in forests, woodlands, and marshes with high humidity, primarily near a body of water.
What do tree frogs eat?
Tree frogs are carnivorous creatures that eat a variety of insects, including flies, ants, crickets, beetles, and moths. However, when they are tadpoles, they primarily eat plants.
Are tree frogs dangerous?
Touching a tree frog can be potentially dangerous to humans and animals because the skin of some species contains a toxin that protects the front from predators. The poison in the skin can cause swelling, nausea, and even death to smaller animals.
Can you keep a tree frog as a pet?
American tree frogs (Hyla cinerea) make good pets, but because of their mildly poisonous skin, you shouldn’t handle them with your bare hands.
What do tree frogs need to survive?
First off, they need a moist, warm environment with humidity of at least 70%. When kept in captivity, tree frogs don’t need direct sunlight but merely a light source that mimics the day/night cycle. They also require a steady diet of insects or worms and a temperature between 65 degrees and 85 degrees Fahrenheit.
What are the differences between tree frogs and toads?
Tree frogs are a group of over 800 tree-dwelling frog species in the family Hylidae. Toads (or true toads) include more than 300 species belonging to the family Bufonidae. The key differences between tree frogs and toads are habitat, size, appearance, reproduction, and behavior.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- The National Wildlife Federation, Available here: https://www.nwf.org/Educational-Resources/Wildlife-Guide/Amphibians/Tree-Frogs
- National Geographic, Available here: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/amphibians/r/red-eyed-tree-frog/
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_frog
- The Spruce Pets, Available here: https://www.thesprucepets.com/american-green-tree-frogs-as-pets-1236810
- Smithsonian National Zoo & Biology Research Institute, Available here: https://nationalzoo.si.edu/animals/whites-tree-frog
- UF Department of Wildlife Conservation and Ecology, Available here: https://ufwildlife.ifas.ufl.edu/frogs/greentreefrog.shtml