White-Crowned Sparrow
Zonotrichia leucophrys
Males learn distinct songs from the community they grew up in and continue to sing in the same dialect as adults.
Advertisement
White-Crowned Sparrow Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Passeriformes
- Family
- Passerellidae
- Genus
- Zonotrichia
- Scientific Name
- Zonotrichia leucophrys
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
White-Crowned Sparrow Conservation Status
White-Crowned Sparrow Facts
- Prey
- seeds, vegetation, and insects.
- Main Prey
- seeds
- Name Of Young
- Chicks
- Group Behavior
- Social
- Fun Fact
- Males learn distinct songs from the community they grew up in and continue to sing in the same dialect as adults.
- Estimated Population Size
- 79 million
- Biggest Threat
- Climate change
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Black and white stripes on their head
- Distinctive Feature
- pink or yellow bills
- Wingspan
- 8.3 to 9.4 inches
- Incubation Period
- 11 to 14 days
- Age Of Fledgling
- 12 days
- Habitat
- Tundra, alpine forests, thickets
- Predators
- large birds like crows, jays, owls, and hawks.
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Lifestyle
- Diurnal
- Type
- Bird
- Common Name
- White-crowned sparrow
- Number Of Species
- 4
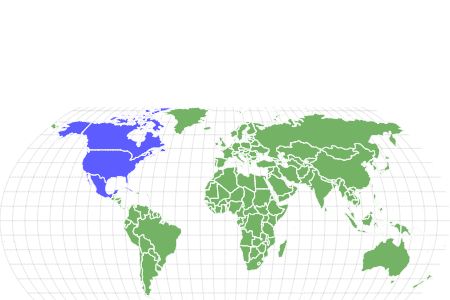
- Location
- North America
- Average Clutch Size
- -2
- Nesting Location
- One the ground near vegetation or a few feet off the ground in a shrub
- Migratory
- 1
View all of the White-Crowned Sparrow images!
“They have different song dialects and prefer to sing the one they grew up with.”
Summary
The white-crowned sparrow (Zonotrichia leucophrys) is a medium-sized New World sparrow native to North America. It inhabits alpine meadows and tundra in Alaska and Northern Canada but chooses to stay in thickets and backyards in its US and Mexico wintering homes. These birds have interesting songs, can fly long distances, and have social personalities. Discover everything there is to know about the white-crowned sparrow!
5 Amazing White-Crowned Sparrow Facts
- Males learn distinct songs from the community they grew up in and continue to sing in the same dialect as adults.
- They are relatively social birds that forage in large flocks during the winter.
- They have lovely, thin whistling songs that mark the sound of spring in the northern regions of its range.
- White-crowned sparrows are strong fliers. Researchers recorded a 300-mile flight in one night!
- This species may be susceptible to climate change in the future.
Where to Find the White-Crowned Sparrow
The white-crowned sparrow lives in at least five countries in North America, including Canada, the United States, Mexico, the Bahamas, and Cuba. Some populations are year-round residents in their Pacific Coast homes in the US, while those who breed in Alaska and Northern Canada migrate south to the United States and Mexico. They inhabit open spaces like tundra, alpine meadows, and forest edges during breeding. In the winter, you can find them in thickets, backyards, and agricultural fields. Look for them hopping about on the ground or tree branches, often in flocks during the winter. And listen for their sweet whistles.
White-Crowned Sparrow Nest
The nest is placed on the ground in a shallow depression near the base of shrubs or grass in the northern regions. Populations further south tend to put theirs in shrubs a few feet off the ground. Females build the nest by forming an open cup made of grass, twigs, weeds, and bark.
They line the inside with soft grass, feathers, and animal hair.
Scientific Name
The white-crowned sparrow (Zonotrichia leucophrys) is from the Passerellidae family, a group of New World passerine birds. Its genus, Zonotrichia, contains five American sparrows, four of which are in North America. Zonotrichia is Ancient Greek for “band” and “hair,” and Leucophrys means “white” and “eyebrow.” There are five recognized subspecies of white-crowned sparrows.
Size, Appearance, & Behavior
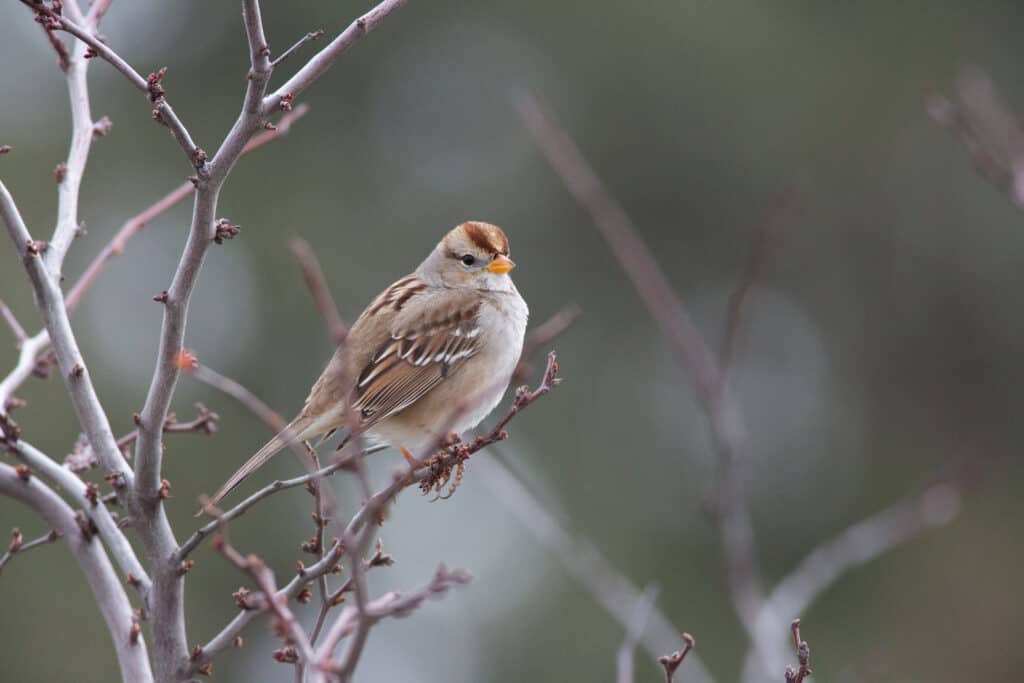

Females lay between two and six (four to five on average) pale green eggs with reddish brown spots. Females incubate by themselves for 11 to 14 days, and both parents assist in feeding the nestlings (mainly insects).
©Brendan Bucy/Shutterstock.com
The white-crowned sparrow is a medium-sized New World sparrow featuring a small bill and a long tail. They measure 5.9 to 6.3 inches long and weigh 0.9 to one ounce, with an 8.3 to 9.4-inch wingspan. Their wings and upper body parts are brown and heavily streaked, while their undersides are gray. They have black and white stripes on their heads, gray faces, and pink or yellow bills.
These sparrows spend their days hopping around on branches or the ground near bushes and trees. They are relatively social, forming pairs during the breeding season and foraging in flocks in winter. They are strong fliers that can travel 300 miles in one night! Their songs are thin, sweet whistles followed by buzzy notes. Males learn distinct songs from the community they grew up in and continue to sing in the same dialect as adults. Some males can be bilingual, singing in two dialects.
Migration Pattern and Timing
White-crowned sparrows are residents or medium-distance migrants. Those that breed in Alaska and Northern Canada migrate to most of the US and Mexico during winter. Populations along the US Pacific Coast and the interior west stay year-round in their environments.
Diet
White-crowned sparrows are omnivores who forage in flocks.
What Does the White-Crowned Sparrow Eat?
They primarily eat seeds, vegetation, and insects. This sparrow mainly eats weed and grass seeds during the winter and insects and spiders in the summer. Throughout most seasons, they feed on buds, moss, flowers, berries, and small pieces of fruit. They forage in flocks outside the nesting season and find their food by hopping and running on the ground. Occasionally, you will find them in low-lying shrubs or mid-air as they jump out to catch flying insects.
Predators, Threats, and Conservation Status
The IUCN lists the white-crowned sparrow as LC or “least concern.” Due to its extensive range and extremely large and stable population, this species does not meet the thresholds for “threatened” status. While nothing immediate threatens their population, the white-crowned sparrow could suffer the effects of climate change in the future. They are highly susceptible to habitat loss from wildfires and endangered young from spring heat waves.
What Eats the White-Crowned Sparrow?
Their primary predators include large birds like crows, jays, owls, and hawks. Snakes are also known to steal eggs from their nest. These sparrows are naturally alert birds who rely on camouflage and their flying ability to defend themselves most of the time. Males are typically more aggressive towards different bird species than their own. They may fly towards intruders with their crown feathers erect and chest puffed out while singing loudly.
Reproduction, Young, and Molting
White-crowned sparrows are monogamous during the breeding season, and some may partner with the same mate during the following season. Females lay between two and six (four to five on average) pale green eggs with reddish brown spots. Females incubate by themselves for 11 to 14 days, and both parents assist in feeding the nestlings (mainly insects). The young fledge the nest seven to twelve days after hatching, but the males continue to care for them while the females begin their second nesting attempt. Populations in the northern regions typically only lay one breed per year, but those further south can have up to four. These sparrows are sexually mature by one-year-old. They have an average lifespan of 2.6 years in the wild but can live up to 13.
Population
The global white-crowned sparrow population is estimated to number 79 million mature individuals. From 1970 to 2017, their population underwent a slight decline of 0.3% per year. However, their numbers have been considered stable for the last ten years, with no extreme fluctuations or fragmentations.
Similar Animals:
View all 108 animals that start with WWhite-Crowned Sparrow FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Where does the white-crowned sparrow live?
The white-crowned sparrow lives in at least five countries in North America, including Canada, the United States, Mexico, the Bahamas, and Cuba.
What is the white-crowned sparrow's habitat?
They inhabit open spaces like tundra, alpine meadows, and forest edges during breeding. In the winter, you can find them in thickets, backyards, and agricultural fields.
How big is a white-crowned sparrow?
The white-crowned sparrow is a medium-sized New World sparrow featuring a small bill and a long tail. They measure 5.9 to 6.3 inches long and weigh 0.9 to one ounce, with an 8.3 to 9.4-inch wingspan.
What do white-crowned sparrows sound like?
Their songs are thin, sweet whistles followed by buzzy notes. Males learn distinct songs from the community they grew up in and continue to sing in the same dialect as adults. Some males can be bilingual, singing in two dialects.
What do white-crowned sparrows eat?
They primarily eat seeds, vegetation, and insects. This sparrow mainly eats weed and grass seeds during the winter and insects and spiders in the summer.
What threatens the white-crowned sparrow?
While nothing immediate threatens their population, the white-crowned sparrow could suffer the effects of climate change in the future. They are highly susceptible to habitat loss from wildfires and endangered young from spring heat waves.
What are the white-crowned sparrow's predators?
Their primary predators include large birds like crows, jays, owls, and hawks. Snakes are also known to steal eggs from their nest.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Red List / BirdLife International, Available here: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22721088/136821496
- Science Direct / Animal Behavior Vol. 31, Issue 1 / Luis F.Baptista, Lewis Petrinovich, Available here: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0003347284803358\
- Science Direct / Animal Behavior Volume 34, Issue 5 / Luis F.Baptista, Lewis Petrinovich, Available here: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S000334728680207X