Utah, whose name comes from the word Ute (meaning “people of the mountains” in an indigenous language), has a long and fascinating history, dating back to the pre-Columbian Pueblo, Utes, and Navajo people, then for a time as a part of the Spanish and Mexican empires, then as a destination for Mormon settlers, and finally as an official American state in 1896. While much of the land is quite hilly and arid, Utah still furnishes quite a lot of ecological and geographic diversity. Its borders encompass dry deserts, deep canyons, massive pine forests, vast wetlands, and towering mountains. Read on to learn more about the animals in Utah. The state of Utah features a diverse ecology and landscape. ©iStock.com/suesmith2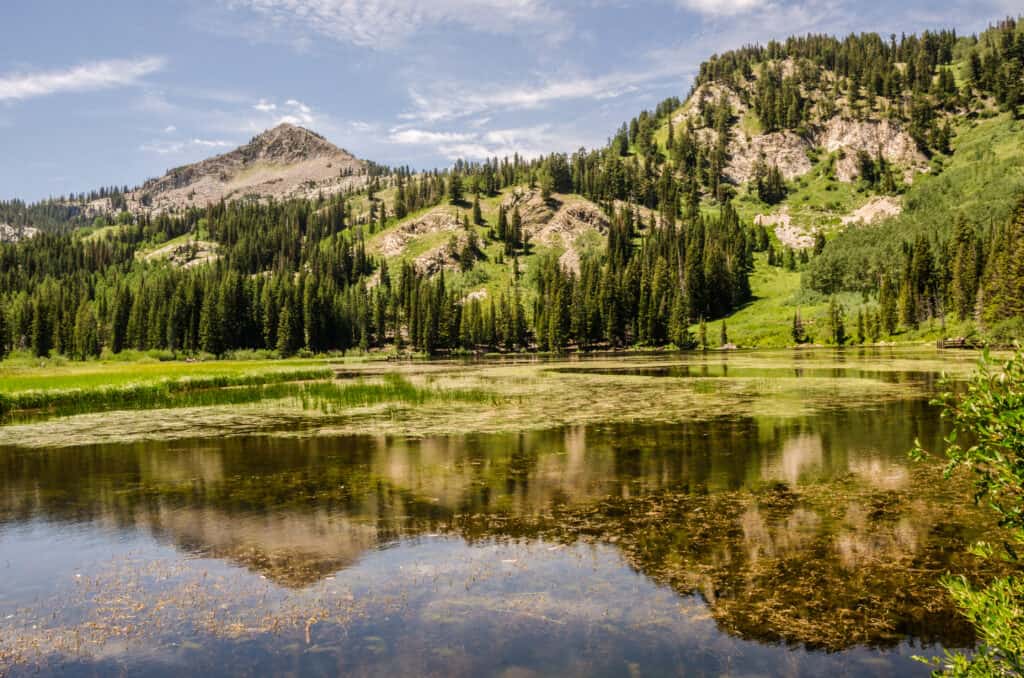
Utah is comprised of three main geographical regions: the Rocky Mountains (which cut through the northeast border near Idaho and Wyoming), the Great Basin along the border with Nevada and Arizona, and the Colorado Plateau near the eastern border with Colorado. The Great Salt Lake, located in the north, is the largest saltwater lake in the entire Western Hemisphere and perhaps the most interesting geographical feature in the entire state; it’s actually the remnant of a more ancient lake called Bonneville. But the state ecology is diverse enough to accommodate many different kinds of wildlife.
The Official Animal of Utah
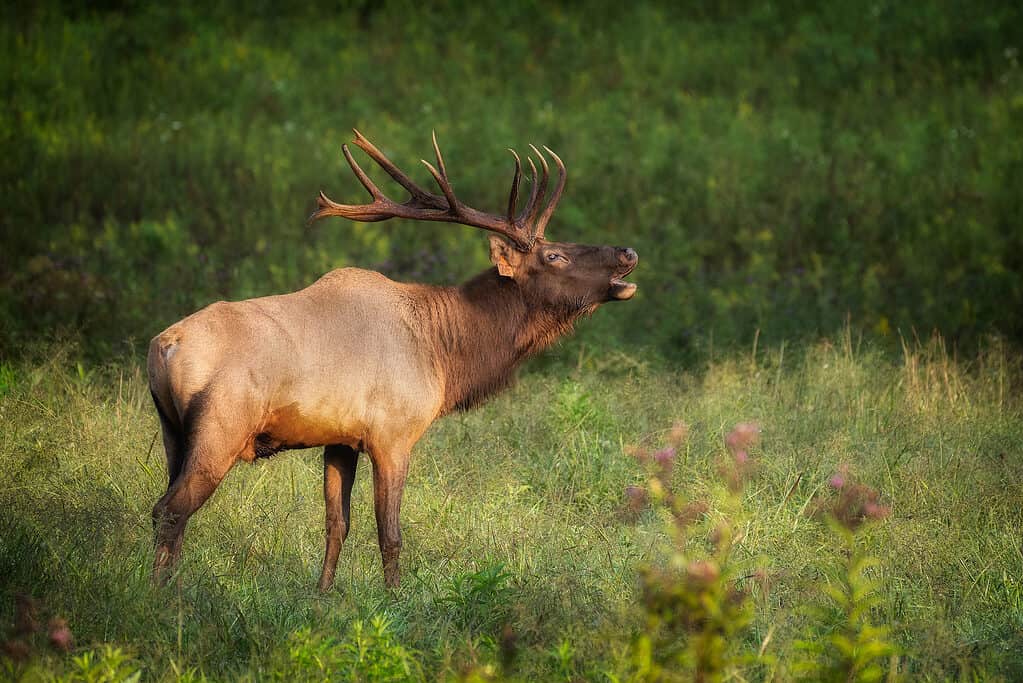

The Rocky Mountain elk is the official state animal of Utah.
©iStock.com/MattCuda
The state of Utah is represented by four distinctive animals. The official state insect is the honey bee, which synergizes well with the state emblem, the beehive, to signify the early state industry. The official state fish is the Bonneville cutthroat trout, an important source of food for early pioneers and Native Americans. The official state bird is the California gull, which has its own monument in Salt Lake City because it helped to consume crickets, which were destroying the crops of the early settlers.
The official state animal of Utah is the Rocky Mountain elk, a subspecies of the elk, which has provided people with meat and leather for many centuries. The elk was once found across most of the state, but it’s now mostly restricted to the mountains.
Where to Find the Top Wild Animals in Utah
Some of the most interesting wildlife in the entire state can be found in the five national parks (representing more than almost any other state in the country) and dozens more state parks and refuges. These state and national parks will cover just about every major geographical area in Utah. Zion National Park features 229 square miles of unique natural sandstone formations with sightings of bighorn sheep, cougars, and many more animals. ©EB Adventure Photography/Shutterstock.com
Zion National Park, located near the southwestern town of Springdale, encompasses 229 square miles of strange natural sandstone formations in Zion Canyon. Visitors can find cougars, bobcats, badgers, bighorn sheep, ring-tailed cats, rodents, and deer. A successful breeding program for the condor, one of the rarest birds in the country, is also present nearby. If you are interested in the arid ecology of Zion Canyon, then you may also want to check out the Canyonlands and Bryce Canyon National Parks, both of them also located in southern Utah.
Antelope Island State Park, located close to Salt Lake City, is the largest island on the lake itself. Although named for the pronghorn antelope, it is most famous for its herd of bison, brought over when the species was nearly extinct. It’s also home to bobcats, mule deer, coyotes, wild sheep, and migratory birds. The Great Salt Lake may be drying – but it is still the destination for millions of migratory birds and waterfowl. ©Bella Bender/Shutterstock.com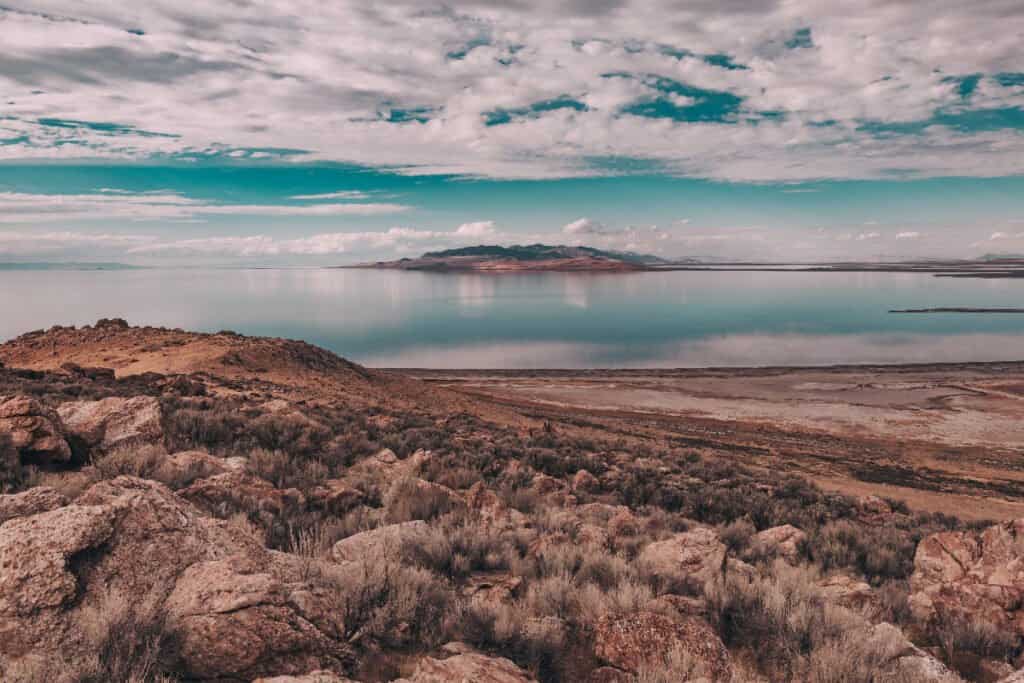
While the high salt content of the water makes it inhospitable for many freshwater animals, the Great Salt Lake is nevertheless a great destination for millions of migratory birds and waterfowl, including stilts, plovers, gulls, sandpipers, ducks, and geese.
The Flaming Gorge National Recreation Area, which straddles the border between Utah and Wyoming, is a 91-mile reservoir and a popular destination for freshwater fishing, including trout, salmon, bass, and burbot. Other types of wildlife include cougars, eagles, elk, moose, bears, antelopes, and other mammals.
The Red Fleet State Park, located just to the south of the Uinta Mountains (a sub-range of the Rocky Mountains), features red slick rock formations and a fossil track of dinosaur footprints. Visitors can also catch a glimpse of hawks, golden eagles, vultures, ospreys, owls, bobcats, coyotes, and deer.
The Dixie National Forest, located in south-central Utah, is the largest national forest in all of Utah. The pinyon and pine forest, interspersed with sparse desert-type plants, provides a habitat for cougars, bobcats, antelopes, prairie dogs, eagles, turkeys, and much more.
Largest Animal in Utah
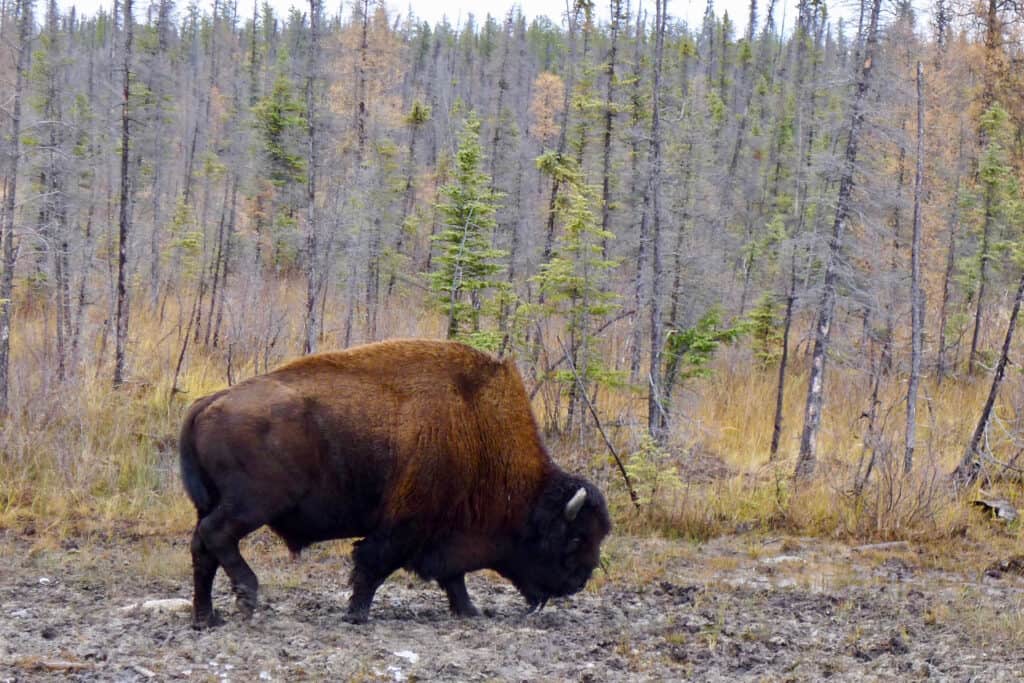

The mountain bison is the largest animal in Utah.
©iStock.com/Peter Loring
The mountain bison, sometimes known as the wood bison, is the largest mammal in Utah, with males weighing around 2,000 pounds. These giants are greater in size than plains bison and have less hair on their forelegs and beards. Because of hunting and the potential for degradation of the breed from mating with plains bison, state officials are taking action to preserve their existence.
Utah’s Henry Mountains is home to one of four pure bison herds that graze freely in North America. 250 – 400 bison, ancestors of the original Yellowstone bison, can be seen there at any given time. The mountain bison herd has 1.2 million acres to roam between Utah and Colorado.
Rarest Animal in Utah
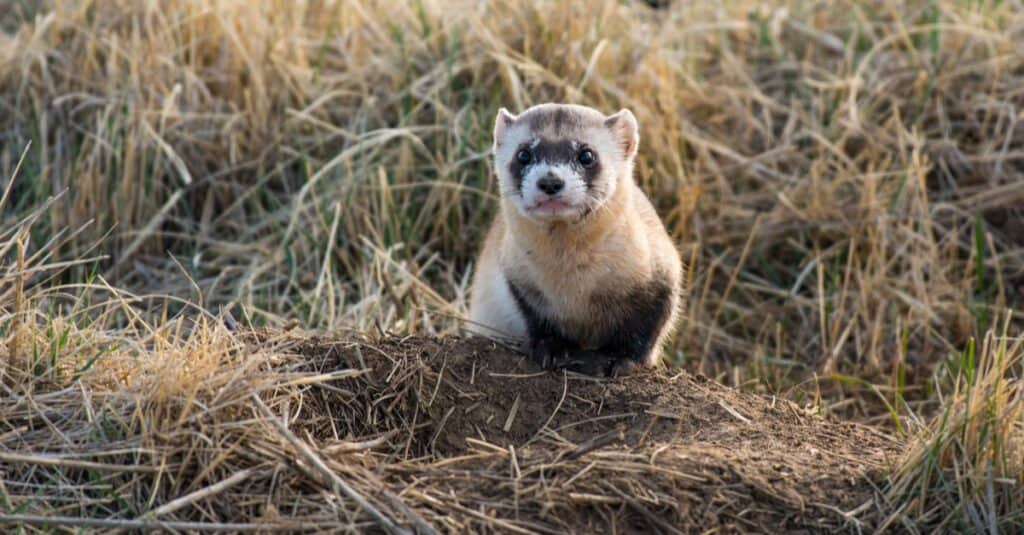

The Black-footed ferret is the only ferret species native to the United States and the rarest mammal in Utah.
©Kerry Hargrove/Shutterstock.com
The black-footed ferret is a member of the weasel family and the only ferret species native to the United States. Easily recognizable by the black mask that makes it look like a bandit, this ferret is the only mammal with habitat in Utah on the Endangered Species List. Ferrets are about the same size as a mink, 18 – 24 inches long and weighing less than three pounds. Their coats are yellow-beige with distinctive black markings on their face, feet, legs, and tails that help the animals to blend into their environment.
Ferrets prey on prairie dogs and take over their burrows for themselves. Prairie dogs make up 90% of their diets, with squirrels, mice, and other rodents making up the rest. Except for the breeding season, ferrets are mostly solitary creatures who spend most of their time underground. This nocturnal animal is known to be vocal and hisses, chatters, and whimpers.
Today, only about 1,000 wild ferrets exist in controlled reintroduction areas. They once roamed 12 American states including Utah – with a range that extended into Canada to the north and Mexico to the south. The ferrets nearly vanished when farmers and ranchers began the wide-scale elimination of prairie dogs, the ferret’s main prey. In 1987, 18 black-footed ferrets were captured to become part of a breeding and reintroduction program.
The Most Dangerous Animals in Utah Today
The state of Utah, and particularly its remote desert and mountainous areas, is home to several dangerous wildlife; some of them have dangerous toxins, others have sharp teeth and claws, while some are just large and aggressive. This list will only include animals that cause direct harm, as opposed to those that spread diseases to people. The Mojave rattlesnake is just one of many dangerous rattlesnakes in Utah. ©iStock.com/Shoemcfly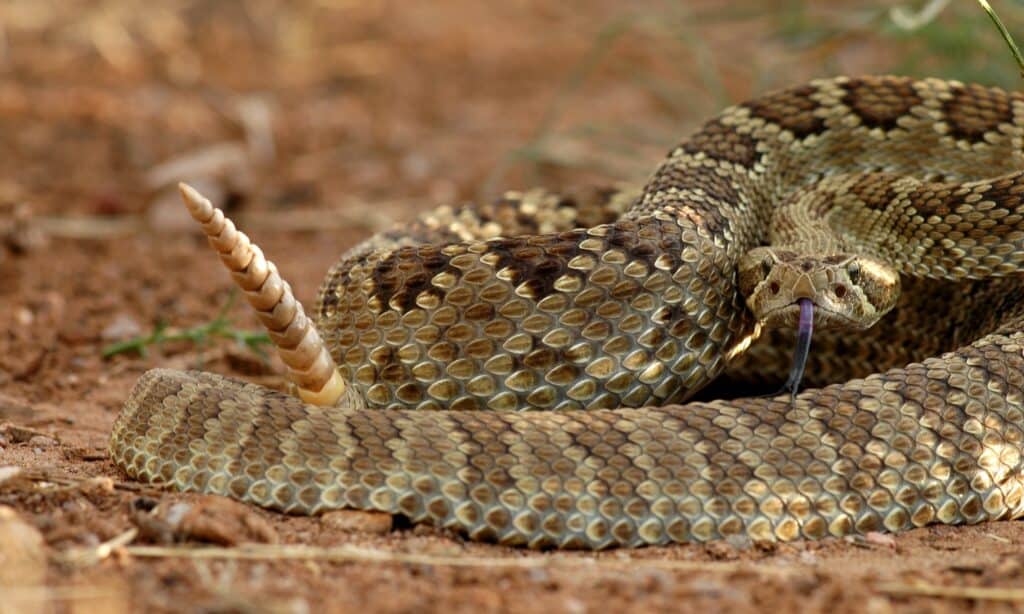
- Rattlesnakes: Utah is home to seven different species of rattlesnakes: the specked rattlesnake, the sidewinder rattlesnake, the Mojave rattlesnake, the western rattlesnake, the midget-faded rattlesnake, the Hopi rattlesnake, and the Great Basin rattlesnake. These snakes are often found in sagebrush, pinyon, and juniper woodlands, sand dunes, grasslands, rocky hillsides, and mountain forests. They can be identified at a quick glance by the elliptical pupils, the presence of a pit above the nostrils, and of course, the rattle on the tail. If you hear a warning rattling, you should stand completely still and try to locate where the sound is coming from first before backing away. The venom itself is quite dangerous because it can lead to pain, swelling, and neurological symptoms. Fortunately, with proper medical care, recovery is normal.
- Black Widow Spider: The adult female of this species, which can be identified by the black body and red markings, has particularly potent venom. Symptoms can include muscle pain, swelling, spasms, nausea, and even mild paralysis, but death is exceptionally rare.
- Recluse Spider: Utah is home to both the desert recluse spider and the brown recluse spider, which have long, thin legs. While generally non-aggressive, their potent venom can destroy tissue and produce lesions on the skin.
- Scorpions: Utah is home to several species of scorpions, including the giant desert hairy scorpion, the black hairy scorpion, the northern scorpion, and the Arizona bark scorpion. While the scorpion’s venom can cause pain, vomiting, and numbness, death does not occur in healthy adults; instead, the very old, young, or immunologically compromised are at the greatest risk of death.
- Wasps and Bees: Utah is home to several types of stinging insects, including hornets, yellow jackets, mud daubers, honeybees, bumblebees, and carpenter bees. While generally producing only pain and swelling, a small number of people may have an allergic reaction to their sting. These people should have epinephrine available just in case of a severe reaction.
- Moose: Because of their non-threatening appearance, people often make the mistake of trying to approach these large deer-like animals. But their massive size, aggressive nature, and huge antlers mean they could potentially kill a person if they decide to charge.
- American Black Bear: The black bear is the largest predator in the entire state (though not necessarily the most dangerous animal). While attacks from these predators are exceptionally rare, you will want to exercise caution in noted bear territory. They may become particularly aggressive in defense of their cubs or their food supply.
- Cougars: While cougars are sometimes feared as dangerous predators, they rarely attack people except in cases where they feel threatened or they’re starving. When they do strike, it’s usually with a bite to the neck.
- Gila Monster: The Gila monster is a relatively large lizard, measuring some 2 feet long. It’s also one of the few poisonous lizards in the world. While the danger of this creature has often been exaggerated, the venom itself is about as toxic as some rattlesnakes. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, nausea, vomiting, weakness, and fainting. Fortunately, they tend to live in underground burrows, and even when encountered, they are not overly aggressive and do not normally bite.
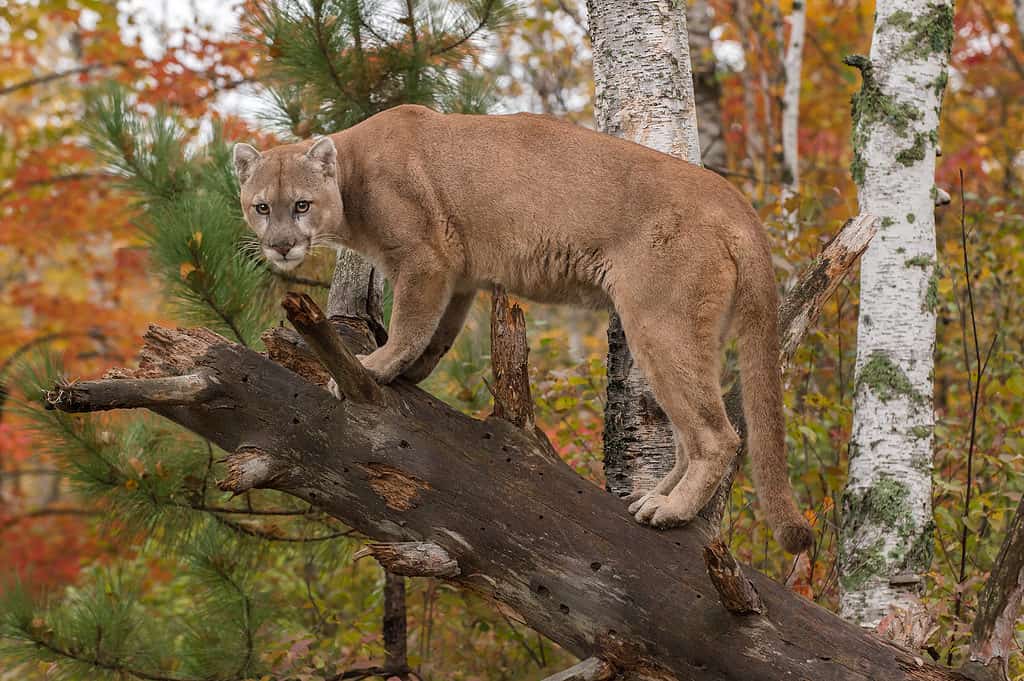

Cougars rarely attack people but they are considered dangerous and could prey on pets.
©Geoffrey Kuchera/Shutterstock.com
Endangered Animals in Utah
The state of Utah maintains its own list of threatened and endangered species, independent of the federal list. Population numbers of these species appear to be falling across the entire state. Grey wolves are among the rarest animals in Utah.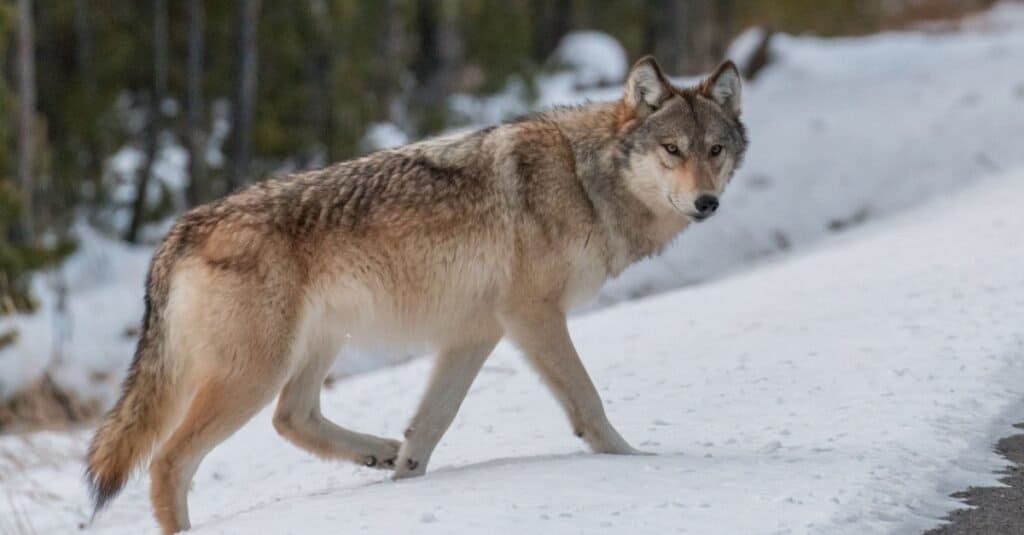
©iStock.com/mtnmichelle
- Prairie Dogs: The Utah prairie dog (and to a lesser extent the white-tailed prairie dog and Gunnison’s prairie dog) is an endangered species in the state of Utah. The main reasons for the decline of these mammals include the loss of suitable prairie habitats and deliberate poisoning by farmers in retaliation for digging holes and eating crops. Only about 3,000 members of this species still remain in the wild.
- Black-footed Ferret: This nocturnal member of the weasel family, which can be identified by the black mask around the eyes and the feet, is now endangered from the decline of its main food source, prairie dogs, and the fur trade.
- Gray Wolf: This is one of the rarest animals in the entire state. While there are no known established packs in Utah, there are occasional sightings as they pass through from the surrounding states.
- Canadian Lynx: The Canadian lynx is a medium-sized feline with long ear tufts, dense fur, and big padded feet. While it’s quite common further north, sightings in Utah are incredibly rare. The closely related bobcat is much more common.
- California Condor: Sporting a massive wingspan and a strange bald head, this is one of the largest and rarest birds in all of North America. Although it nearly became extinct in the late 20th century from habitat destruction, poisoning, and poaching, condors have survived in southwestern Utah thanks to strong conservation efforts.
- Southwestern Willow Flycatcher: This small migratory bird, which can be identified by its green body, darker wings, and lighter underside, is vulnerable to habitat loss and a decline of its native nesting trees. It’s estimated that only a few hundred breeding pairs currently remain in the wild.
- Mexican Spotted Owl: Identified by the white spots covering its body, this is a subspecies of the spotted owl. It is currently threatened by habitat loss from the logging industry across parts of its range.
- Desert Tortoise: Native to the arid Mojave Desert of southwestern Utah, the desert tortoise spends most of its life in burrows and rock shelters to keep cool and reduce water loss. It is vulnerable to extinction from the combined effects of human activity and diseases.
- Greenback Cutthroat Trout: Characterized by a red throat and a green back, this is the easternmost subspecies of the cutthroat trout. Because of overfishing, water diversion, and toxic runoff, it now occupies only a fraction of its former habitat.
- Kanab Ambersnail: Native to wetlands, springs, and seeps near the city of Kanab, this subspecies of amber snail has a strange translucent shell, which appears amber when empty. It is currently threatened by habitat loss and limited populations.
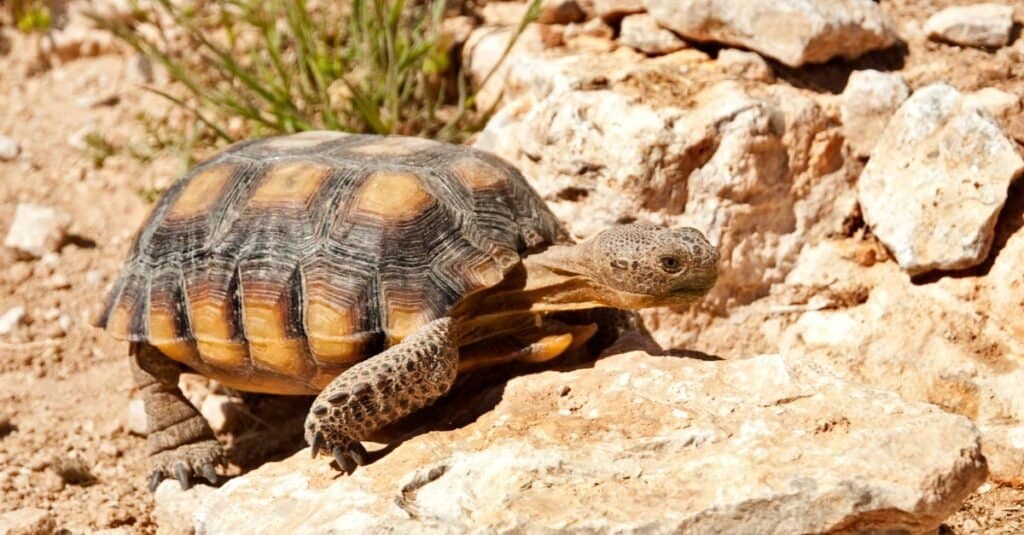

The desert tortoise is native to the desert regions of Utah and is among the rarest animals in the state.
©Darren J. Bradley/Shutterstock.com
Native Plants in Utah
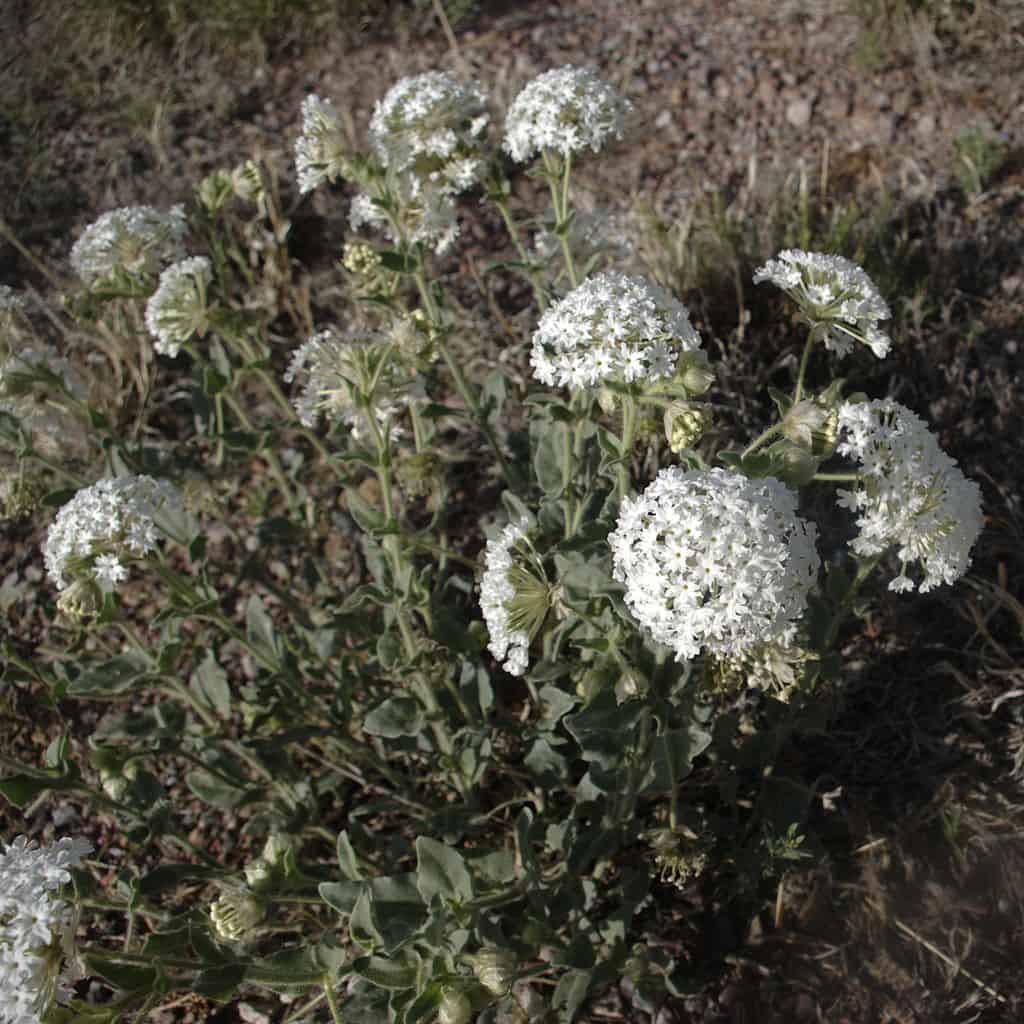

Fragrant sand verbena is native to Utah and often called Four O’clocks because its flowers open in the evening and close in the morning.
©JerryFriedman / CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons – License
Utah is diverse in terms of geography and climate, and the state exhibits a variety of regions and ecosystems. Several thousand plants are native to the state of Utah. Some native plants in Utah include mountain lover, creeping barberry, and fragrant sand verbena, among others.
Also, Utah is home to over 240 species of trees, many of which are native to the area. Some beautiful trees native to the state of Utah include Gambel oak, chokecherry, and ponderosa pine, among others.
The Utah State Flag
The flag of Utah features some of the official state animals. It also features the official Utah motto and other state symbols.
More Articles Related to Utah
Read about:
- extinct animals that lived in Utah.
- the highest point in Utah.
- the top waterfalls in Utah.
- the common species of ticks in Utah.
- the coldest place in Utah.
Utahn Animals

Admiral Butterfly
Stunningly beautiful wings

Allosaurus
Allosaurus is the official state fossil of Utah because of the abundant number of fossils found in the state.

Barosaurus
If a barosaurus were alive today, it could stand on its hind legs and look in a 5th floor apartment window.

Beewolf wasp
They hunt bees

Blue Belly Lizard
This species can detach its tail to escape from predators

Burrowing Owl
The burrowing owl lives in underground burrows

Cactus Wren
It is the largest wren in the United States

California Condor
They are the largest bird in North America

California Kingsnake
A full-grown California kingsnake can be about 3.5 feet long, though there are some cases in Mexico of the snake being almost twice this size.

Cinnamon Bear
A newborn cinnamon bear weighs 1/2 pound -- about the same as a large apple.

Common Yellowthroat
The Common Yellowthroat stays close to the ground and uses stealth to survive!

Diplodocus
Their long tales could have been used as a whip!

Flea
Adult fleas can jump up to 7 inches in the air

Gopher Snake
Gopher snakes can reach up to 9 feet long.

Green Snake
There are two types of green snakes: smooth green snakes and rough green snakes

Harris’s Hawk
Their vision is eight times better than a human's

Jackrabbit
They can run as fast as 45 mph.

Kangaroo Mouse
The Kangaroo Mouse is a tiny mouse that stands and hops around on its hind legs, much like a kangaroo.

Kit Fox
The kit fox is the smallest canid in North America.

Kokanee Salmon
A non-anadromous type of sockeye salmon

MacGillivray’s Warbler
The complicated story of how MacGillivray’s Warblers got their name involves three ornithologists, a physician and a compromise.

Mealybug
They have a symbiotic relationship with ants.

Midget Faded Rattlesnake
They're also called horseshoe rattlesnakes thanks to the shape of their markings.

Mockingbird
Mockingbirds are incredible mimics that can learn hundreds of songs!

Mojave Rattlesnake
"The Mojave rattlesnake is the most venomous rattlesnake in the world."
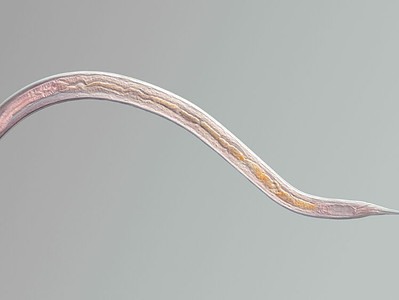
Nematode
Nematodes range in size from 1/10 of an inch to 28 feet long

Orb Weaver
Females are about four times the size of males

Owl
The owl can rotate its head some 270 degrees

Polyphemus Moth
The Polyphemus moth doesn’t and can't eat, except when it's a caterpillar!

Rainbow Grasshopper (Dactylotum bicolor)
They have strikingly bright colors

Rat Snakes
Rat snakes are constrictors from the Colubridae family of snakes.

Rooster
Will mate with the entire flock!

Smallmouth Bass
A fierce fighter!

Smokybrown Cockroach
Has up to 45 eggs per egg case

Tiger Trout
As tiger trout are sterile, they cannot produce offspring. However, they do have relatively long lifespans and can live up to 10 years in captivity.

Tree Cricket
They make music with their wings

Uinta Ground Squirrel
The squirrel is named after the Uinta Mountains, which are part of the Rocky Mountain range and are found in Utah and Wyoming.

Western Blind Snake
Western blind snakes are flourescent in black light!
Utahn Animals List
- Admiral Butterfly
- Allosaurus
- Barosaurus
- Beewolf wasp
- Blue Belly Lizard
- Burrowing Owl
- Cactus Wren
- California Condor
- California Kingsnake
- Cinnamon Bear
- Common Yellowthroat
- Diplodocus
- Dire Wolf
- Flea
- Gopher Snake
- Green Snake
- Harris’s Hawk
- Jackrabbit
- Kangaroo Mouse
- Kit Fox
- Kokanee Salmon
- MacGillivray’s Warbler
- Mealybug
- Midget Faded Rattlesnake
- Milk Snake
- Mockingbird
- Mojave Rattlesnake
- Nematode
- Night Snake
- Orb Weaver
- Owl
- Polyphemus Moth
- Rainbow Grasshopper (Dactylotum bicolor)
- Rat Snakes
- Red Racer Snake
- Rooster
- Sidewinder
- Smallmouth Bass
- Smokybrown Cockroach
- Southeastern Blueberry Bee
- Styracosaurus
- Swallowtail Butterfly
- Tiger Trout
- Tree Cricket
- Uinta Ground Squirrel
- Western Blind Snake
- Yellowish Cuckoo Bumblebee (formerly Fernald’s Cuckoo Bumblebee)
Animals in Utah FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What types of animals are there in Utah?
Utah is home to many different types of mammals, including bats, rodents, prairie dogs, bighorn sheep, goats, hares, deer, and other deer-like animals, and carnivores (like foxes, badgers, and weasels). It’s also home to quite a few lizards, snakes, turtles, frogs, and toads. The Great Salt Lake teems with migratory birds and water birds, while the rest of the state has lots of songbirds and birds of prey. There are also thousands of different insect species and other invertebrates.
What dangerous wildlife is in Utah?
Utah is home to seven species of rattlesnakes, several venomous spiders, a few scorpions, quite a few stinging insects, and the Gila monster. People should also be wary of black bears, cougars, and other predators or large creatures.
What kinds of animals live in Salt Lake City, Utah?
Salt Lake City harbors some very common animals such as raccoons, rodents, rabbits, badgers, foxes, bats, skunks, deer, foxes, songbirds, and waterfowl.
Are there caribou in Utah?
Caribou (also known as reindeer) are not found as far south as Utah, but the state does have some moose and other deer-like species.
What rattlesnakes are in Utah
Utah is home to 7 types of rattlesnakes. That includes 5 unique species of rattlesnakes and several subspecies. The unique species of rattlesnakes that live in Utah include:
- Mojave Rattlesnakes
- Praire Rattlesnakes
- Western Rattlesnakes
- Speckled Rattlesnakes
- Sidewinder Rattlesnakes












