Colorado may be most known for having some of the most towering peaks in the Rocky Mountains, but the Denver Museum of Natural History has identified eight distinct ecosystems within the state that vary from grasslands and forest to wetlands and semi-desert shrub-lands that evoke the deserts of neighboring New Mexico. There are eight distinct ecosystems in the state of Colorado. ©iStock.com/SeanXu
The native wildlife here is as diverse as the ecosystems. There are roughly 750 invertebrate species that call Colorado home — and that includes large grazers like the bison and bighorn sheep as well as vicious predators like mountain lions and bears. From the Rocky Mountains all the way down to the grasslands, these wild frontiers allow for very diverse ecosystems to flourish.
The Official Animal of Colorado
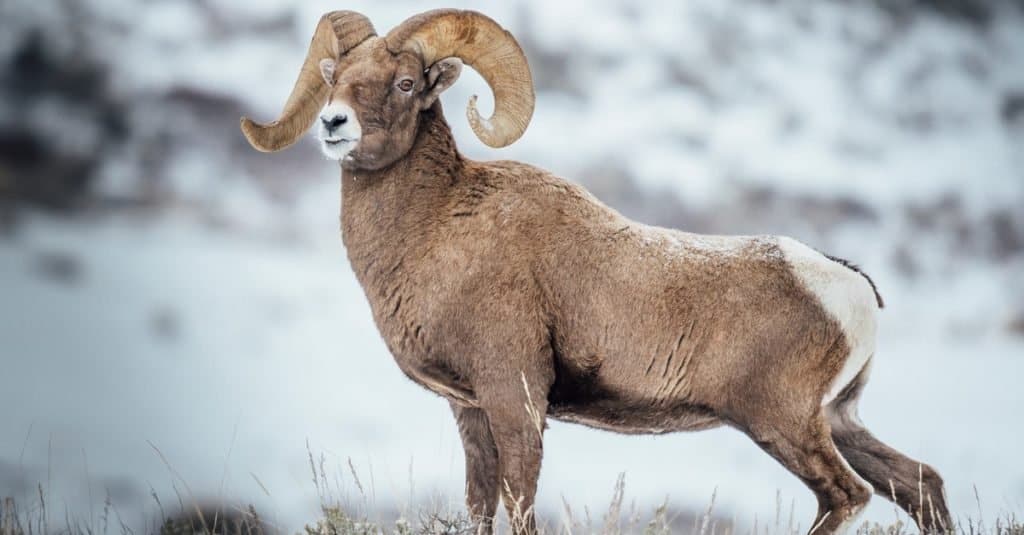

The bighorn sheep is the official national animal of Colorado.
©John Raptosh/Shutterstock.com
Colorado’s official animal is understandably an animal that’s emblematic of the Rocky Mountains. The Rocky Mountain bighorn sheep was declared the national animal in 1961. These sociable creatures only exist in the Rockies, but they’ve unfortunately been reduced to endangered status thanks to their appeal to big game hunters.
Colorado’s state bird was actually declared 30 years before the state animal. The lark bunting is migratory and can be widely seen throughout the state from April until September. They call both the plains of Colorado and elevations of up to 8,000 feet their home.
Where To Find The Top Wild Animals in Colorado
Fitting its diverse variety of ecosystems, Colorado is home to some excellent camping and houses 42 state parks and four national parks — while each of them is beautiful in its own right, there are a few that are worthy of the particular spotlight. Bison can be seen at the Rocky Mountain Arsenal National Wildlife Refuge outside of Denver, Colorado. ©Tim Malek/Shutterstock.com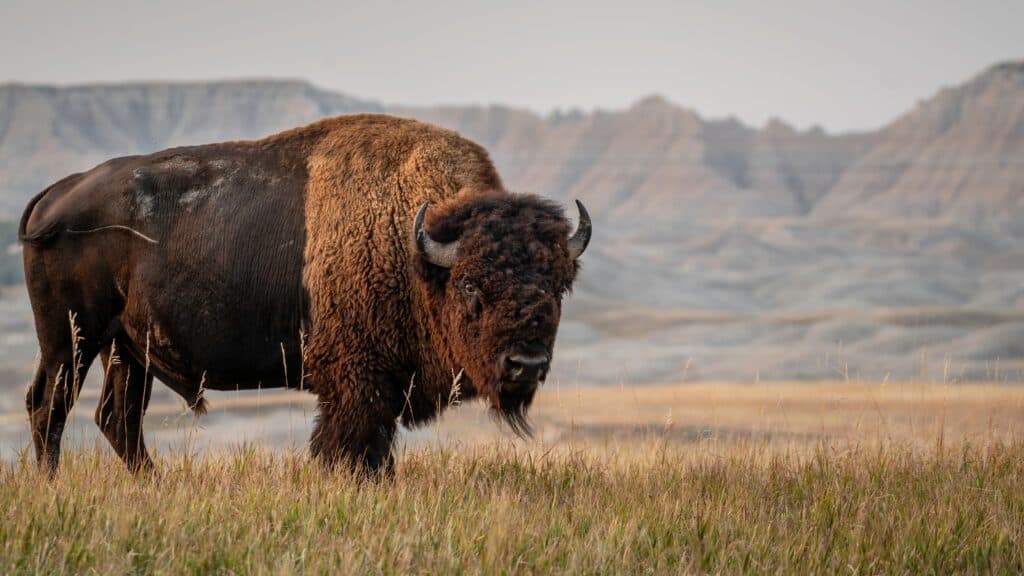
- The Horseshoe and Morain sections of Rocky Mountain National Park are the best places for seeing elk, but these majestic animals are common all throughout the park. This national park offers some of the best places to camp in Colorado.
- Bison were once among the rarest and most endangered animals in Colorado, but you can now find them just outside of Denver at Rocky Mountain Arsenal National Wildlife Refuge. It’s also home to coyotes, mule deer, and even bald eagles during the winter season.
- South Platte River Trail in the winter is going to offer the best opportunity to see bald eagles, but it’s a respectable place for bird-watching all year long. Notable species include kestrels and red-tailed hawks.
- The state parks in Denver can be a great opportunity to spot wildlife. State Forest State Park is recognized as the “Moose Capital” of Colorado, but these large herbivores aren’t the only wildlife here. Beavers, foxes, and black bears can also be found.
- Great bighorn sheep are becoming one of the rarest species in Colorado, but they’re most common at the Great Sand Dunes National Park. Coyotes and bobcats are some of the most common predators, but small rodents like ground squirrels are also easy to spot.
Wild Animals in Colorado
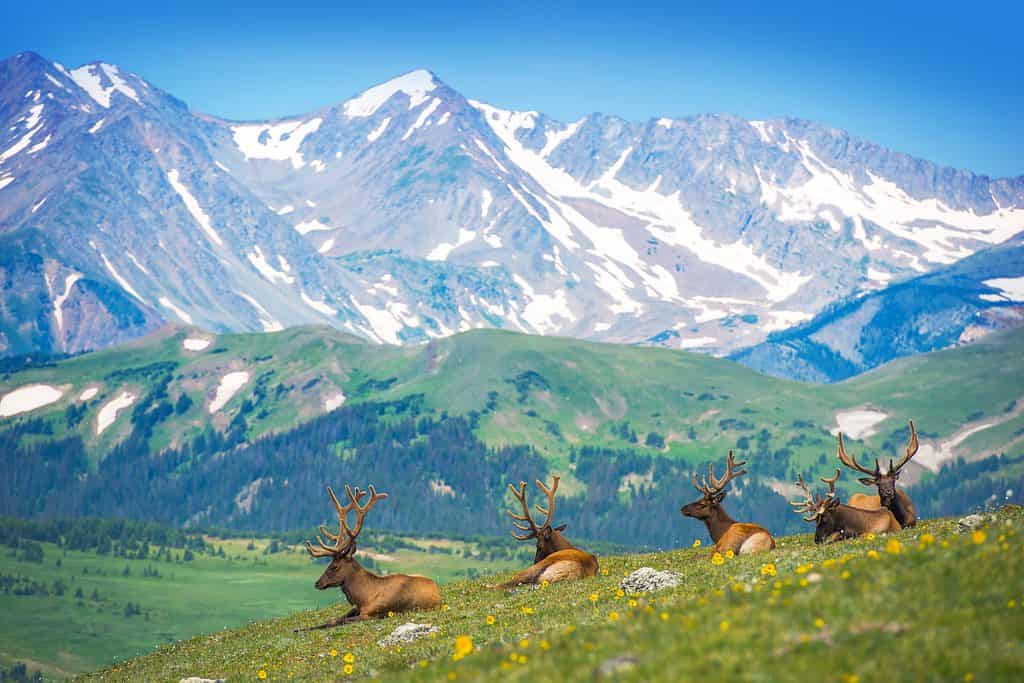

Elk are native to Colorado and can be seen in mountainous regions.
©Virrage Images/Shutterstock.com
The wildlife of Colorado is similar to the wildlife found in many other Mountain States like Montana and Wyoming. The most notable large herbivores are the bighorn sheep, elk, bison, and moose. Major predators in these ecosystems include mountain lions, black bears, and foxes.
Small creatures constitute some of the most critical wildlife in many Colorado ecosystems. Prairie dogs are considered a keystone species because the tunnels they dig are used by roughly 150 different animals. The beaver plays a similarly critical role in Colorado’s wetlands ecosystems — and they’re becoming an increasingly common sight in urban areas as well.
Largest Animal in Colorado
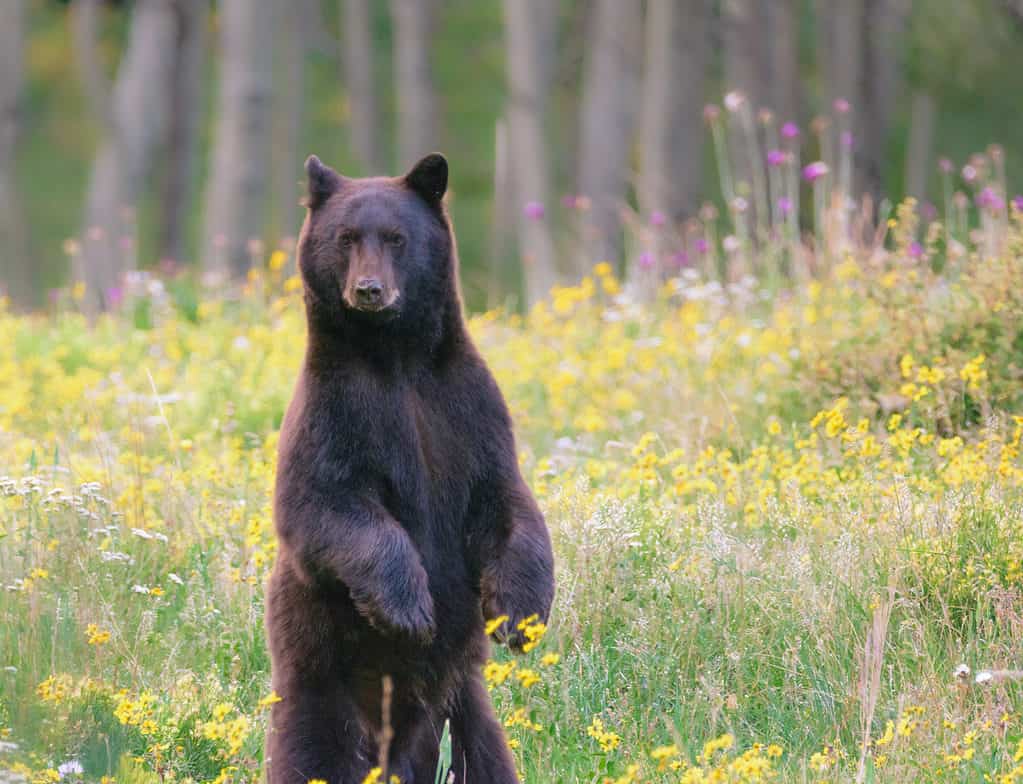

The black bear is the largest animal in Colorado.
©Constance Mahoney/Shutterstock.com
The black bear is the largest animal in Colorado today – inhabiting most of the forested areas of the state, including the Rocky Mountains. The average black bear stands at five feet on its back legs and walks on all fours at three feet. Males weight up to 600 pounds while females are much smaller at 200 pounds.
Black bears are omnivores whose diet consists of 80% plants, 15% insects, and 5% animal matter. Fruits, nuts, honey, and other plants are their favorites – but they sometimes eat fish, mice, squirrels, and other small mammals.
The Most Dangerous Animals In Colorado Today
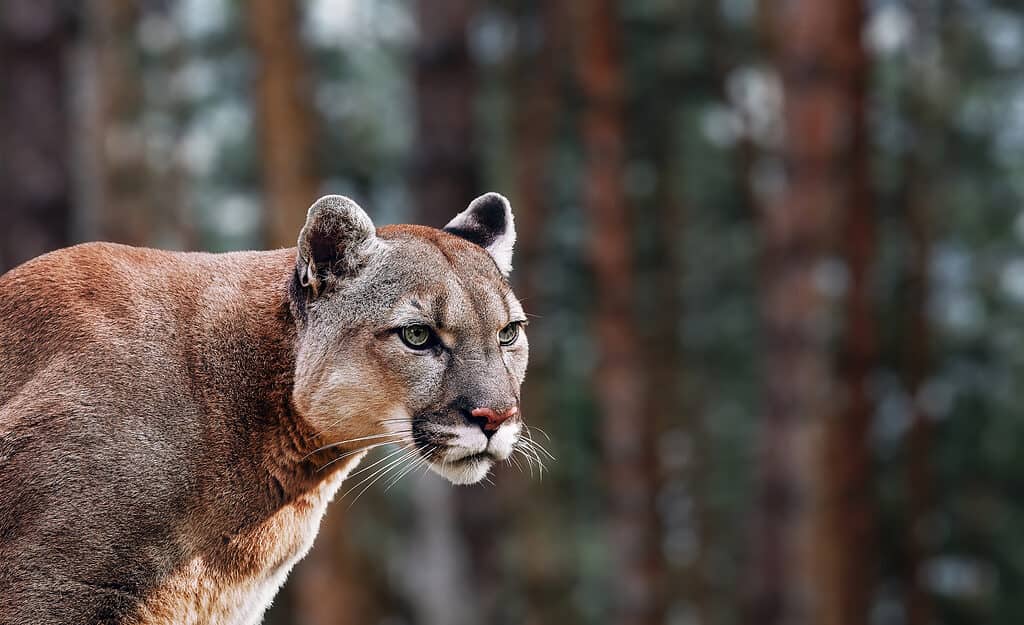

Mountain lions are among the most dangerous animals in Colorado.
©Evgeniyqw/Shutterstock.com
- Mountain goats are relatively common sights in the mountains — and while they’re not predators, they’ve been known to gore hikers with their horns when they feel threatened.
- Black bears also don’t actively pursue humans, but they’re known for being aggressive if they feel like their cubs are being threatened.
- Mountain lions are one of the rarer predators, but they’ve been spotted all over the state. Encountering them out on a hiking trail isn’t uncommon, but there were only 25 Colorado mountain lion attacks documented between 2000 and 2021.
Rarest Animal in Colorado
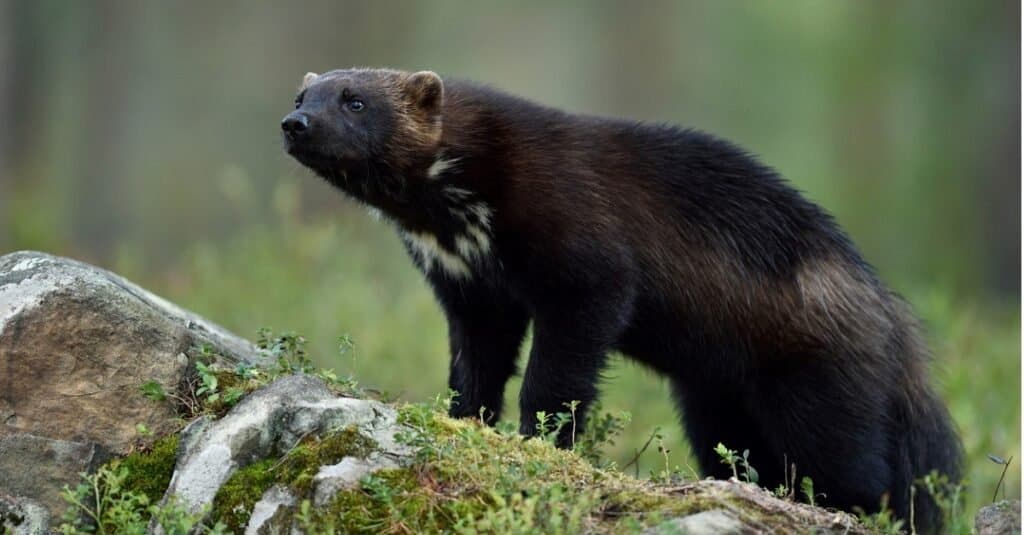

The Wolverine is one of the rarest animals in colorado.
©iStock.com/ErikMandre
The wolverine is the largest member of the weasel family with short, rounded ears, a broad head, and a stocky body – these animals resemble little bears with long bushy tails. Males are larger than females and weigh up to 35 pounds. They are solitary creatures who eat a variety of animals including small rodents, rabbits, porcupines, ground squirrels, birds, eggs, fish, carrion, and some plants.
The last documented sighting of a wolverine in Colorado occurred in 2009 but there may be a few living in the state. The animals require so much habitat that 100 animals would probably be at full capacity. After the successful reintroduction of elk, bighorn sheep, and river otters, the wolverine is a candidate for reintroduction even though some experts believe they are making their way back to the state without human intervention.
Endangered Animals In Colorado
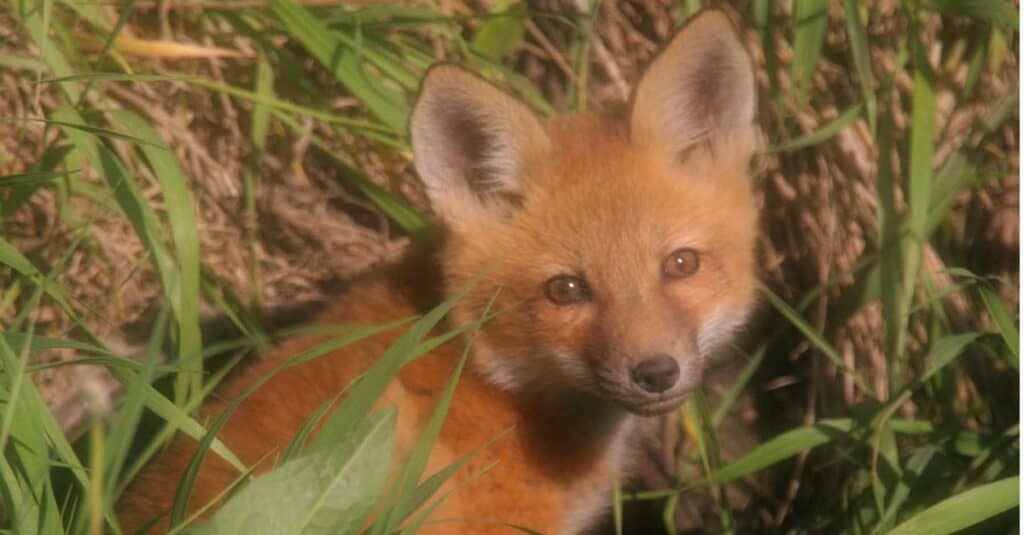

The kit fox is native to Colorado and is currently endangered.
©iStock.com/JackVandenHeuvel
Colorado is home to multiple endangered species. Big game like the bighorn sheep and bison were once endangered but are now recovering. Some of the most notable endangered wildlife include:
- Black-footed ferret: The only federally endangered mammal in Colorado, they rely on prairie dogs for both housing and food.
- Humpback chub: Native to the Colorado River, they’ve adapted to survive incredibly turbulent currents.
- Wolverine: It’s strange to see a wolverine in Colorado, and they were once believed to be extinct in the state. One of the rarest native species, it’s believed that as many as 100 might be surviving in the state unnoticed.
- Kit fox: A strange native species of fox most notable for its small frame and strange, deep-set eyes.
Zoos in Colorado

The Cheyenne Mountain Zoo is the highest zoo in the United States.
©University of College/Shutterstock.com
The Cheyenne Mountain Zoo in Colorado Springs is a beautiful zoo situated on a hilly, 146-acre site. 800 animals can be viewed in the Australia Walkabout, All About Giraffes, Encounter Africa, Rocky Mountain Wild, and more. There is a sky ride that offers a birds-eye view from a chairlift. Other notable Colorado zoos include:
- Denver Downtown Aquarium is home to many attractions that capture the thrill of the natural world. The aquarium sustains more than 500 animal species in over one million gallons of water.
- The Wild Animal Sanctuary is a 1,214-acre animal sanctuary in Keenesburg, Colorado which specializes in animal rescue. The sanctuary cares for large predators which have been ill-treated or which might have been euthanized.
- Denver Zoo is an 80-acre zoological garden featuring 4,000 animals from 700 species from all over the world. The Denver Zoo is notable for its efforts to restore bison to tribal lands.
- Pueblo Zoo is a 25-acre zoo that is home to over 420 animals of more than 140 species. This facility, located in Pueblo, Colorado, is also known for the five original historic buildings featuring beautiful craftsmanship and masonry work of the 1930s.
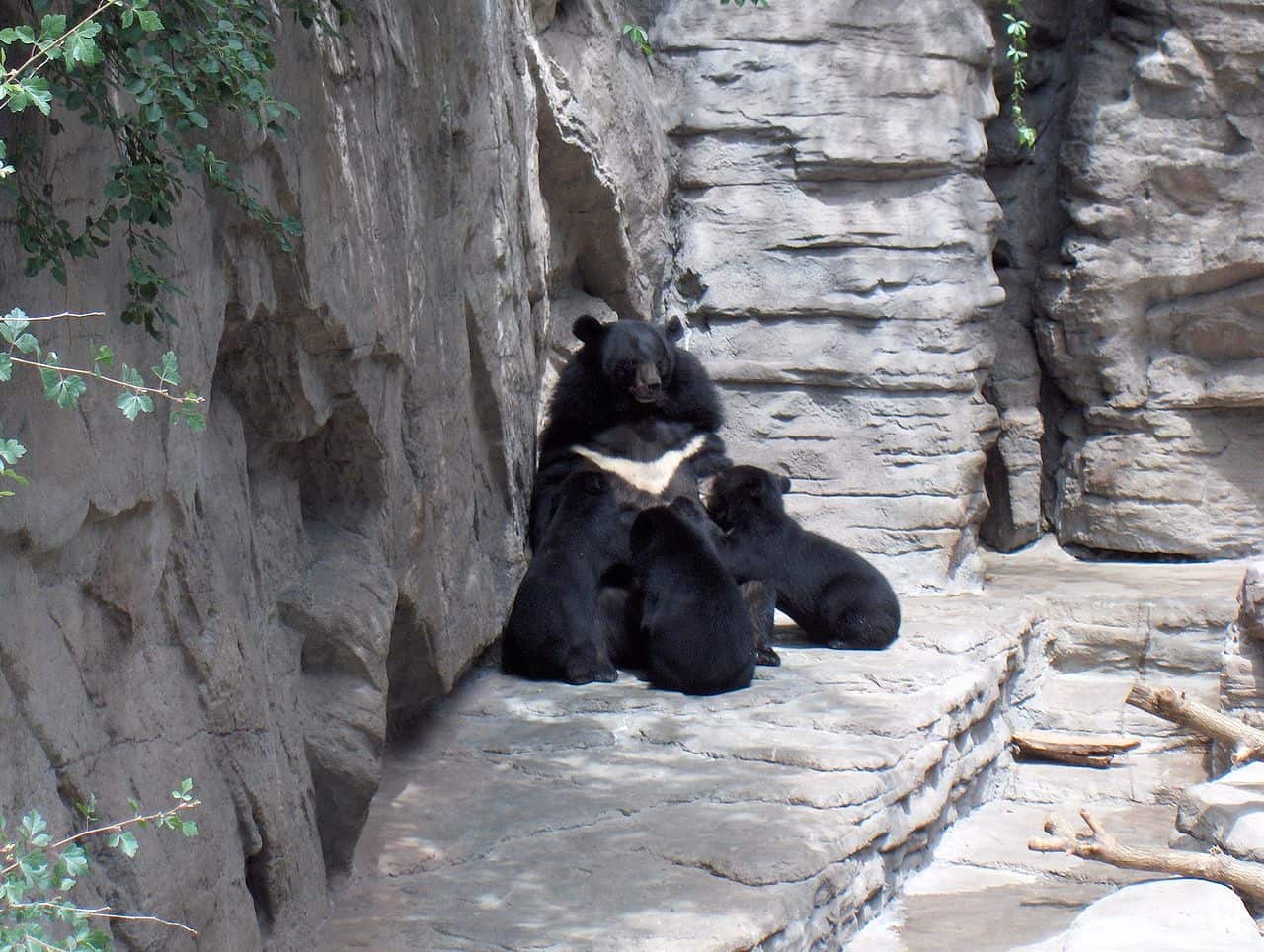

Asiatic Black Bear
with young at Denver Zoo
©self, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons – License
Native Plants in Colorado
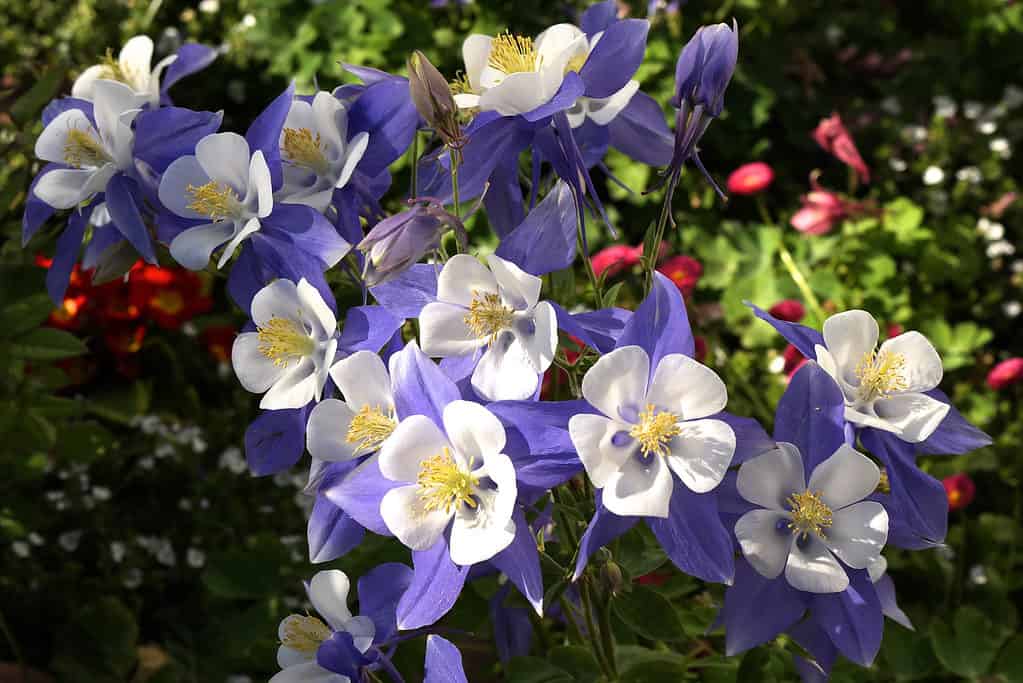

Colorado blue columbine (Aquilegia caerulea) is the state flower of Colorado.
©iStock.com/Linda Jo Heilman
Colorado may be known for its mountainous landscape, but there’s no shortage of beauty when you look at the plants and flowers found in the state. The state flower is the Colorado blue columbine, a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family and native to the Rocky Mountains.
From black-eyed Susans to Colorado blue columbine, explore this list of native plants in Colorado, and then go exploring to spot as many as you can.
Beetles in Colorado
Colorado is a state of soaring heights, deep snow drifts, farmland and windy days. Its airy and haunting beauty is only matched by its diversity in wildlife. If you’re interested in unique and fascinating beetles, Colorado’s the place to go!
More Articles Related to Colorado
Read about:
- Extinct animals that lived in Colorado
- Ticks in Colorado
- The snowiest place in Colorado
- The most common roaches in Colorado
- The best national parks in Colorado
- Amazing waterfalls in Colorado
- The highest point in Colorado
- Ten clear lakes in Colorado
- The largest flathead catfish ever caught in Colorado
- The largest common carp ever caught in Colorado
- The largest King salmon ever caught in Colorado
- The best fishing spots in Colorado in the summer
- The deepest lake in Denver, Colorado
- The best dog parks in Aurora, Colorado
- The best dog parks in Colorado Springs, Colorado
- The largest and most dangerous snakes in Colorado
- The largest black bear ever caught in Colorado
- The largest pronghorn ever caught in Colorado
- The largest lake trout caught in Colorado
- The largest American eel ever caught in Colorado
- The Largest Snake River Cutthroat Ever Caught in Colorado
Coloradan Animals

Admiral Butterfly
Stunningly beautiful wings

Allosaurus
Allosaurus is the official state fossil of Utah because of the abundant number of fossils found in the state.

Arctic Char
Arctic char is the northern-most fish; no other fish lives anywhere further north!

Armyworm
They are so named because they "march" in armies of worms from one crop to another in search of food

Beewolf wasp
They hunt bees

Brachiosaurus
Palentologists originally believed that brachiosaurus lived in the water, but they lived on land.

Burrowing Owl
The burrowing owl lives in underground burrows

California Kingsnake
A full-grown California kingsnake can be about 3.5 feet long, though there are some cases in Mexico of the snake being almost twice this size.

Cinnamon Bear
A newborn cinnamon bear weighs 1/2 pound -- about the same as a large apple.

Common Yellowthroat
The Common Yellowthroat stays close to the ground and uses stealth to survive!

Diplodocus
Their long tales could have been used as a whip!

Eastern Fence Lizard
Females are usually larger than males.

Eastern Woodrat
The eastern woodrat mating ritual involves a potentially deadly fight between the male and female before reproduction begins!

Flea
Adult fleas can jump up to 7 inches in the air

Gopher Snake
Gopher snakes can reach up to 9 feet long.

Harris’s Hawk
Their vision is eight times better than a human's

Kangaroo Mouse
The Kangaroo Mouse is a tiny mouse that stands and hops around on its hind legs, much like a kangaroo.

Kit Fox
The kit fox is the smallest canid in North America.

Kokanee Salmon
A non-anadromous type of sockeye salmon

MacGillivray’s Warbler
The complicated story of how MacGillivray’s Warblers got their name involves three ornithologists, a physician and a compromise.

Massasauga
The name “Massasauga” comes from the Chippewa language, meaning “Great River Mouth”.

Mealybug
They have a symbiotic relationship with ants.

Midget Faded Rattlesnake
They're also called horseshoe rattlesnakes thanks to the shape of their markings.

Mockingbird
Mockingbirds are incredible mimics that can learn hundreds of songs!
Nematode
Nematodes range in size from 1/10 of an inch to 28 feet long

Orb Weaver
Females are about four times the size of males

Owl
The owl can rotate its head some 270 degrees

Plains Hognose Snake
The plains hognose snake gets its name from the upturned end of its snout.

Polyphemus Moth
The Polyphemus moth doesn’t and can't eat, except when it's a caterpillar!

Rainbow Grasshopper (Dactylotum bicolor)
They have strikingly bright colors

Rat Snakes
Rat snakes are constrictors from the Colubridae family of snakes.

Rooster
Will mate with the entire flock!

Smallmouth Bass
A fierce fighter!

Smokybrown Cockroach
Has up to 45 eggs per egg case

Texas Night Snake
The Texas night snake has vertical pupils to help it see better at night.

Tiger Trout
As tiger trout are sterile, they cannot produce offspring. However, they do have relatively long lifespans and can live up to 10 years in captivity.

Tree Cricket
They make music with their wings

Western Tanager
They migrate farther north than any other tanager.
Coloradan Animals List
- Admiral Butterfly
- Allosaurus
- Arctic Char
- Armyworm
- Beewolf wasp
- Brachiosaurus
- Burrowing Owl
- California Kingsnake
- Cinnamon Bear
- Common Yellowthroat
- Diplodocus
- Eastern Fence Lizard
- Eastern Woodrat
- Flea
- Gopher Snake
- Harris’s Hawk
- Kangaroo Mouse
- Kit Fox
- Kokanee Salmon
- MacGillivray’s Warbler
- Massasauga
- Mealybug
- Midget Faded Rattlesnake
- Milk Snake
- Mockingbird
- Nematode
- Orb Weaver
- Owl
- Plains Hognose Snake
- Polyphemus Moth
- Rainbow Grasshopper (Dactylotum bicolor)
- Rat Snakes
- Redear Sunfish
- Rooster
- Smallmouth Bass
- Smokybrown Cockroach
- Supersaurus
- Swallowtail Butterfly
- Texas Night Snake
- Tiger Trout
- Tree Cricket
- Western Tanager
- Yellowish Cuckoo Bumblebee (formerly Fernald’s Cuckoo Bumblebee)
Native Wildlife in Colorado: A Complete Guide FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What rattlesnakes are in Colorado?
Colorado is home to four types of rattlesnakes. While in the state you may see desert massasaugas, western massasaugas, prairie rattlesnakes, and midget faded rattlesnakes.
What kind of animals are in Colorado?
Eagles, bighorn sheep, garter snakes, and pika call the mountains home — while big game like elk and bison roam the valleys and forests at the foot of the Rockies. Beavers call the wetlands home along with a variety of birds and amphibians.
What is the most rare animal in Colorado?
The black-footed ferret is the most endangered mammal in Colorado because of a combination of disease and a drop in the population of prairie dogs. That’s because the ferrets rely on these rodents for both shelter and as a source of food.
What mammals are found in Colorado?
All kinds of mammals call Colorado home. The sub-desert region includes rodents like prairie dogs and predators like coyotes, while you’ll find mammals like elk and bison throughout the plains and forests. Bighorn sheep, black bears, and cougars all become more common as you rise in elevation through the Rocky Mountains.
What wildlife lives in Colorado mountains?
Bighorn sheep are the most iconic — and surprisingly among the most dangerous — animals in the Rocky Mountains, but they’re joined by dangerous predators like the black bear and mountain lion as well as the strange creature known as the pika.
What other states are the Rocky Mountains in?
Other than Colorado, the Rocky Mountains are found in the states of Wyoming, Montana, Idaho, New Mexico and Utah.








